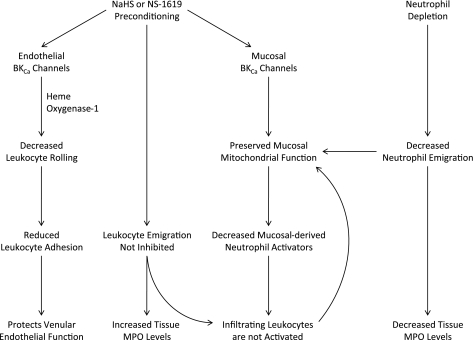
Fig. 9.
Summary diagram illustrating the role of endothelial and mucosal BKCa channels as mediators of the effects of antecedent treatment with NaHS or NS-1619 (NaHS or NS-1619 Preconditioning) to limit I/R-induced leukocyte rolling and adhesion and preserve mucosal mitochondrial function. Neutrophil depletion with ANS prior to the onset of I/R also preserved mucosal mitochondrial function. Since I/R-induced neutrophil infiltration (assessed using tissue MPO activity as a marker) was prevented by ANS treatment, but not by administration of NaHS or NS-1619, our results suggest that infiltrating neutrophils may not be activated to produce collateral injury in the postischemic intestine of animals preconditioned with NaHS or NS-1619. Although the postischemic increase in TNF-α was not attenuated by NaHS or NS-1619 preconditioning, multiple chemotactic agents are released and act in concert to promote neutrophil in the interstitial space after intestinal I/R. It is possible that release of at least some of these neutrophil activators may be abrogated by preconditioning, thereby limiting activation of extravasated leukocytes.