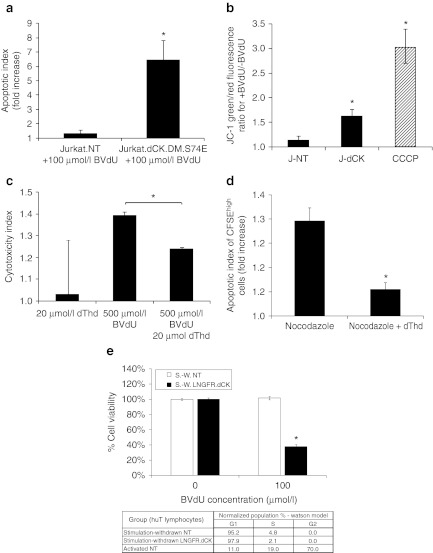
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of cell killing by activated bromovinyl-deoxyuridine (BVdU) in Jurkat cells expressing thymidine-activating deoxyCytidine Kinase (dCK). (a) Jurkat cells-expressing dCK.DM.S74E demonstrate a significant increase in the induction of apoptosis as measured by Annexin-V staining following 5 day treatment with 100 µmol/l BVdU (apoptotic index measures the fold increase in Annexin-V positive cells in BVdU-treated cells over untreated control). (b) Loss of mitochondrial inner membrane potential in Jurkat cells transduced with LV-dCK.DM.S74E and cultured in the presence or absence of 100 µmol/l BVdU for 48 hours (J-NT, nontransduced; J-dCK, dCK.DM.S74E-transduced; CCCP, 50 µmol/l carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone mitochondrial membrane potential disrupter). Increase in the ratio of green to red fluorescence of the JC-1 dye correlates with mitochondria disruption (error bars represent SD; data acquired in duplicate; *indicates statistically significant difference compared to nontransduced controls, P < 0.05). (c) Molt-4 cells transduced with dCK.DM.S74E and nontransduced controls were cultured in the presence or absence of 20 µmol/l dThd, 500 µmol/l BVdU, or both, for a period of 2 days. Viability was assessed by the MTS assay. Percent cell killing was calculated and normalized to nontreated controls. Cytotoxic index was calculated as the ratio of percent cell killing in dCK.DM.S74E-transduced cells to percent cell killing in nontransduced control cells for each treatment group (error bars represent SE of the mean; each analysis was performed in triplicate; *indicates statistically significant difference, P < 0.005). (d) Molt-4 cells transduced with dCK.DM.S74E and nontransduced controls were labeled with 10 µmol/l CFSE and cultured in the presence or absence of 100 µmol/l BVdU, and in the presence or absence of 0.1 µg/ml nocodazole, 20 µmol/l dThd, or both for 4 days. Induction of apoptosis in CFSEhigh nondividing cells was assessed by Annexin V staining. (Apoptotic index measures the fold increase in Annexin-V positive cells in BVdU-treated cells over untreated control. Error bars represent SD; data was acquired in duplicate; *indicates statistically significant differences between groups, P < 0.05). (e) Human T cells transduced with LNGFRΔ.dCK.DM.S74E vector and nontransduced controls were cultured with anti-CD3/CD28 beads and IL-2 stimulation removed (stimulation-withdrawn (S.-W.) cells). Cell-cycle distribution was assessed by propidium iodide staining of fixed cells, and analyzed by flow cytometry, with the results tabulated. Cell viability following a 4-day exposure of the cells to 100 µmol/l BVdU was assessed by the MTS assay. (Error bars represent SE; data acquired in quadruplicate; *indicates statistically significant differences between BVdU-treated and untreated groups, P < 0.01).