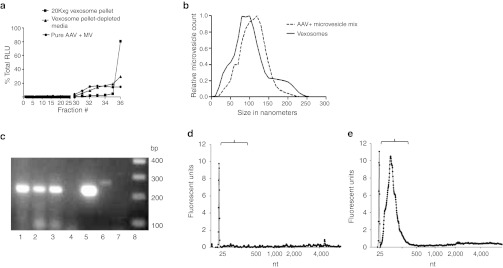
Figure 2.
Characterization of vexosomes. (a) Functional vexosomes are contained in different gradient fractions than standard adeno-associated virus (AAV). The following three samples were loaded onto different 6–18% iodixanol step gradients: (i) standard AAV2-Fluc vectors mixed with microvesicles (MV), (ii) vexosomes pelleted at 20,000g (20K × g AAV2-Fluc vexosome pellet), (iii) vexosome-depleted media (20K × g vexosome pellet-depleted media). After centrifugation the gradients were fractionated and 5 µl aliquots from each fraction were used to transduce separate wells of 293T cells. Two days later, cell lysates were examined for Fluc activity to determine which fractions contained functional vector. (b) Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of iodixanol gradient fraction #36 from the standard AAV2-Fluc vector mixed with purified 293T-derived microvesicles (dashed line) and of iodixanol fraction #36 from the vexosome sample (solid line). (c) Detection of GAPDH mRNA in vexosome sample using reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. The PCR products were visualized on a 2% agarose gel. Lane 1, 108 AAV genome copies (g.c.) from fraction #36 of iodixanol gradient vexosomes pelleted at 20K× g; lane 2, 108 AAV g.c. from fraction #36 of iodixanol gradient of vexosome 20K × g-depleted media; lane 3, #36 of iodixanol gradient, pure AAV (108 g.c.) mixed with 293T microvesicles sample; lane 4, pure AAV (108 g.c.); lane 5, HeLa cell total RNA used as template for RT-PCR (positive control); lane 6, HeLa cell total RNA used as template (no RT step, negative control); lane 7, no template control; lane 8, DNA ladder. (d,e) Bioanalyzer analysis of RNA in (d) conventionally purified AAV-Fluc vector sample (108 g.c.) or (e) 108 g.c. from vexosome sample. Black bracket indicates area of small RNA species.