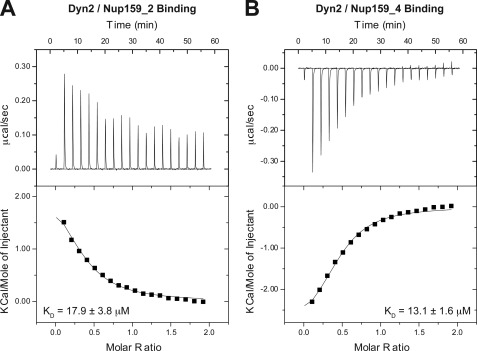
FIGURE 6.
The Dyn2 interactions with Nup159 pep2 and pep4 occur in a 1:1 stoichiometry and exhibit similar affinities but differ in their thermal binding modes. A, 17 × 2 μl of 1 mm Nup159 pep2 was injected into 200 μl of 100 μm Dyn2. The thermogram (upper panel) displays μcal/sec over the injection period (min). B, 17 × 2 μl of 1 mm Nup159 pep4 was injected into 200 μl of 100 μm Dyn2. Dyn2 binding to Nup159 pep2 (A) displayed an endothermic binding isotherm, whereas Dyn2 binding to Nup159 pep4 (B) showed exothermic binding. Thermograms (upper panels) were integrated, and the resulting isotherm was fit to a one-site binding model (lower panels) through iterative fitting. KD values presented (inset, lower panel) are the average of three independent experiments: Dyn2-Nup159 pep2, KD = 17.9 ± 3.8 μm, ΔH = 2500 cal/mol, ΔS = 31 cal/mol/deg, n = 0.33 sites; Dyn2-Nup159 pep4, KD = 13.1 ± 1.6 μm, ΔH = −4000 cal/mol, ΔS = 8.6 cal/mol/deg, n = 0.39 sites.