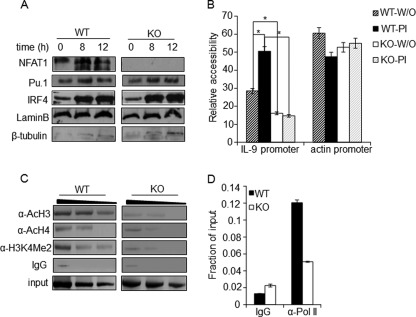
FIGURE 4.
NFAT1 regulates chromatin architecture at the IL-9 promoter. A, nuclear extracts were prepared from Th9 cells differentiated from WT and NFAT1−/− (KO) mice and stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for the indicated time. The nuclear levels of Pu.1, IRF4, lamin B (nuclear control), and β-tubulin (cytosolic control) were analyzed by immunoblotting with the respective antibodies. B, nuclei isolated from either unstimulated (W/O) or PI-stimulated WT and NFAT1−/− (KO) Th9 cells were left untreated or subjected to MNase digestion. Relative chromatin accessibility at the promoters of the IL-9 and actin promoter (as a control for the accessible region) was measured by qRT-PCR using specific primers. The results are represented as the ratio of PCR product obtained from digested samples normalized to the PCR products from undigested samples and mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3); *, p < 0.05. C and D, PMA/ionomycin-stimulated Th9 cells from WT and NFAT1−/− (KO) mice were used for the ChIP assay with antibodies against acetylated histones (AcH3, AcH4, and H3K4Me2), RNA-Pol II, or control IgG. qRT-PCR with primer spanning the IL-9 promoter locus (−366/+48) was used to detect the precipitated DNA and represented as negative images of EtBR-stained gels (C) or relative to the amount in total chromatin (input) as fraction of input (D). All data are representative of at least three independent experiments.