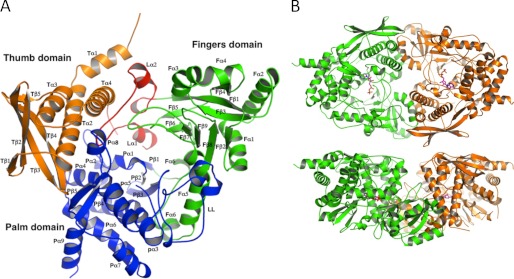
FIGURE 3.
Structure of the type C NIS synthetase AsbB. A, overall monomer structure of AsbB shows the numbering scheme. The N-terminal thumb domain (orange, 1–136) is composed of four α-helices (a small N-terminal helix followed by a three-helix bundle) and a four-stranded anti-parallel β-sheet. A long loop (red, 137–183) consisting of three small α-helices and two short α-helices with connecting turns is a part of the substrate binding pocket and separates the thumb domain and the fingers domain. Sandwiched between these domains, the extended loop is stabilized by a number of hydrophilic and hydrophobic interactions involving several well conserved residues (supplemental Fig. 2). The fingers domain (green, 184–384) contains five α-helices and an 8-stranded antiparallel β-sheet that twists to form part of the cup-shape binding/active site. The C-terminal palm domain (blue, 380–601) of 10 α-helices and five β-strands (2 β-sheets; 3 stranded antiparallel and a β-ribbon) connects the other two domains and forms a major part of the substrate-binding pocket. B, shown is the dimeric form of AsbB as the asymmetric unit. The top model shows the large substrate binding pocket; the bottom model is rotated around the x axis by 90° relative to the top model and highlights the pocket formed by the two dimers.