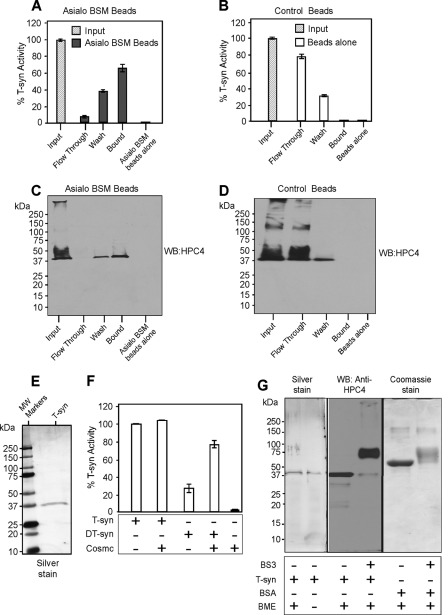
FIGURE 1.
Characterization of recombinant HPC4-T-synthase and His-sCosmc. HPC4-sT-syn was co-expressed with wild type membrane-bound Cosmc in Hi-5 insect cells and His-sCosmc was also expressed in the same system. Both tagged proteins were purified from the media. A-D, HPC4-sT-syn preparation was characterized for its activity with asialo-BSM beads or beads alone. Pulldown experiments were carried out and HPC4-sT-syn bound to asialo-BSM beads as determined either by activity of T-synthase (A and B) or Western blotting (WB) against HPC4 (C and D). In A and B, two replicate experiments were performed, and the data represents the average of the two independent experiments. Error bars ± 1 S.D. from the average. C and D show a representative example of two independent experiments. E, recombinant HPC4-sT-syn (T-syn) purified with asialo-BSM beads was resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized by silver stain. F, in vitro refolding shows that Cosmc restores the activity of asialo-BSM purified heat-denatured HPC4-sT-syn (DT-syn) but not the activity of the T-syn. Each experiment was performed in duplicate, two replicate experiments were performed, and the data represents the average of all experiments. Error bars ± 1 S.D. from the average. G, silver-stained gel of HPC4-T-synthase under reducing or non-reducing conditions. HPC4-T-synthase (0.25 μg) was cross-linked by using BS3 cross-linker followed by SDS-PAGE and Western blot for HPC4. In parallel, control BSA (6 μg) was treated with BS3 and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie stain. BME, β-mercaptoethanol.