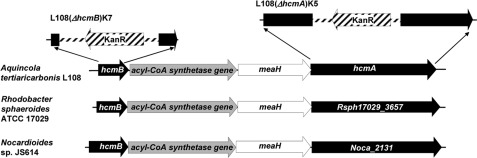
FIGURE 2.
HCM genetic structure. Comparison of the 4.5-kb hcm gene environment in A. tertiaricarbonis L108 with the closely related sequences of R. sphaeroides ATCC 17029 (NCBI locus tag Rsph17029_3654 to Rsph17029_3657) and Nocardioides sp. JS614 (Noca_2129 to Noca_2131). Genes of the HCM subunits hcmB and hcmA are drawn in black; the acyl-CoA synthetase gene is gray; and meaH, encoding for a MeaB-like chaperone, is white. The Ez-Tnp5<Kan-2>Tnp inserts from the two knock-out mutants L108(ΔhcmB)K7 and L108(ΔhcmA)K5 are shown fasciated, whereas the disrupted genes stay black. The different gene length and overlapping intensity between meaH and hcmA are based on the real data from NCBI. An identical organization of the hcm operon was also detected in the genomes of strains M. petroleiphilum PM1, R. sphaeroides KD131, S. novella DSM 506, Marinobacter algicola DG893, Mesorhizobium alhagi CCNWXJ12-2 and X. autotrophicus Py2.