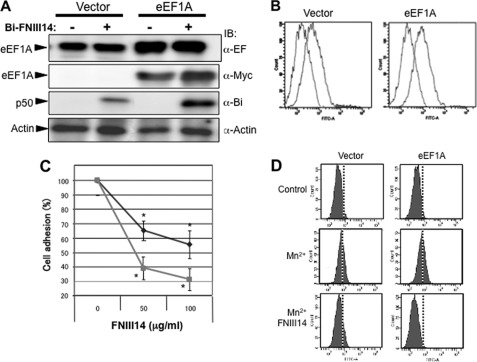
FIGURE 6.
Effect of enforced expression of eEF1A on cellular susceptibility to peptide FNIII14. WI38VA13 cells were transfected with an empty vector (Vector) or eEF1A and then examined as follows. A, cells were affinity labeled with (+) or without (-) biotinylated FNIII14 and then subjected to immunoblot (IB) analysis using anti-EF1A (α-EF), anti-myc (α-Myc), anti-biotin (α-Bi), and anti-actin (α-Actin) antibodies. B, cells treated as indicated were incubated with preimmune normal IgG (blue lines) or anti-EF1A monoclonal antibody (red lines) as primary antibody and with FITC-labeled anti-mouse IgG and then subjected to flow cytometry. C, inhibition of cell adhesion to the fibronectin substratum by peptide FNIII14 was assayed using cells transfected with an empty vector (blue line with ♦) or with eEF1A (red line with ■). Each point represents the mean ± S.D. of triplicate determinations. One of three or four individual experiments is shown. *, p < 0.01 compared with control (without FNIII14). D, inhibition of Mn2+-dependent β1-integrin activation by peptide FNIII14 was assayed by flow cytometry using AG89, a monoclonal antibody against an active conformation of β1-integrins. Data shown in A, B, and D are representative of three individual experiments.