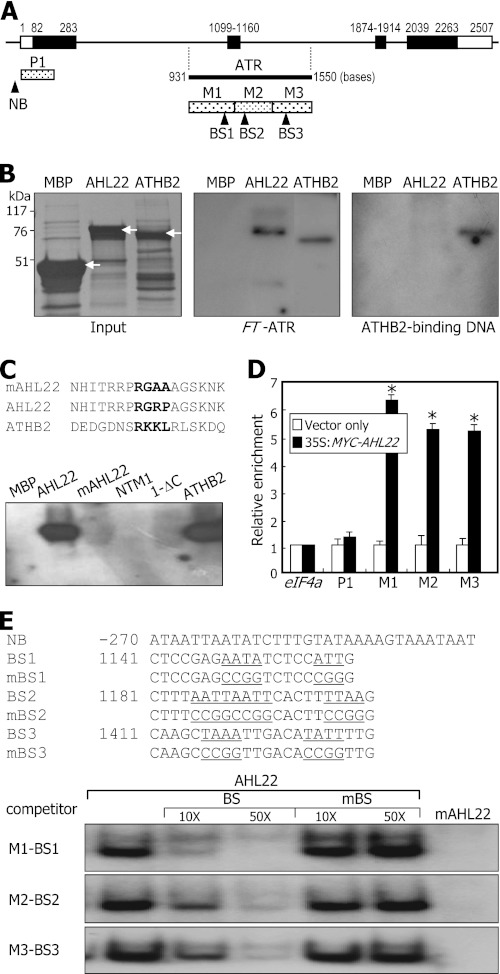
FIGURE 2.
Binding of AHL22 to FT-ATR. A, location of ATR in FT locus. Black bars indicate exons, and white bars indicate untranslated regions. The FT-ATR was dissected into 3 sequence regions, M1 to M3. P1 is a control DNA fragment. Putative BSs of AHL22 were selected according to the rule proposed previously (40). NB, nonbinding sequence. B, AHL22 binding to FT-ATR. Recombinant AHL22 and ATHB2 proteins were prepared as MBP fusions in E. coli cells (left panel, white arrows). The same amounts of proteins shown on the protein gel and 32P-labeled DNA fragments were used in the in vitro binding assays (middle panel). The ATHB2-binding sequence was also assayed (right panel). C, effects of core sequence mutations on AHL22 binding to FT-ATR. The core sequence of the AT-hook motif (RGRP) was mutated to RGAA, resulting in mAHL22 (upper panel). NTM1 and ATHB2 transcription factors were included as controls in the assays (lower panel). D, ChIP assays on AHL22 binding to FT-ATR. The 35S:MYC-AHL22 transgenic plants grown on MS-agar plates for 2 weeks were used. Primer pairs specific to M1, M2, and M3 sequences were used. Three measurements were averaged and statistically treated (t test, *p < 0.01). Bars indicate mean ± S.E. E, EMSA on AHL22 binding to FT-ATR. The BS sequences were mutated to verify specific binding, resulting in mutated BS (mBS) sequences (upper panel). Increasing amounts of unlabeled BS or mutated BS oligonucleotides were added to the assay mixtures (lower panel).