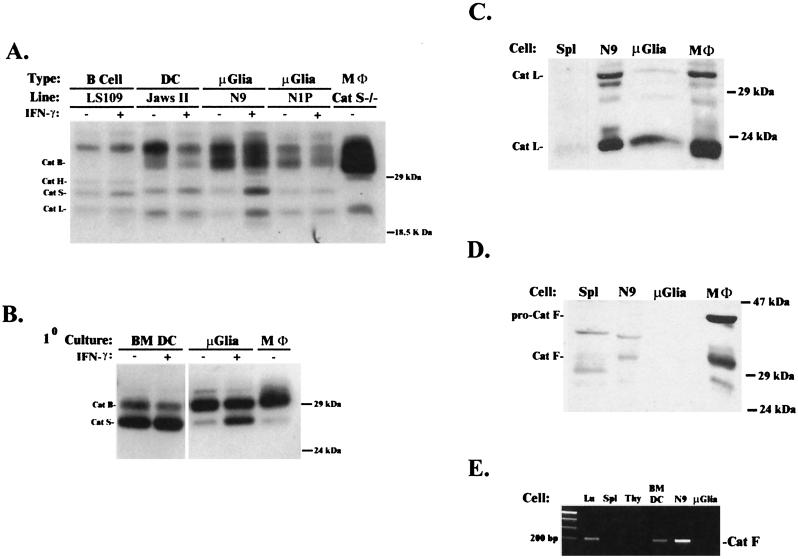
Figure 4.
Microglia express cathepsins S and L but not F. (A and B) Cell lysates from cell lines (LS109, Jaws II, N9, and N1P), primary cultures of neonatal microglia (μGlia), bone marrow-derived DC (BM DC), splenocytes (Spl), and peritoneal macrophages (MΦ) were labeled with 125I-JPM and analyzed by 13% SDS/PAGE. All APC express active cathepsins S and B. Up-regulation of cathepsin S with IFN-γ is seen in many, but not all, cell lines. (C) Cathepsin L Western blot of cell lysates showing the active form of cathepsin L in N9 cells, microglia, and macrophages but not splenocytes. (D) Cathepsin F Western analysis of the same blot as in C demonstrating expression of active cathepsin F in macrophages and, to a lesser extent, in N9 cells. Microglia, but not other cells, were stimulated with IFN-γ (100 units/ml) for 72 h before analysis to maximize expression of cathepsin F. (E) RT-PCR of cathepsin F from mouse tissues and cell suspensions. Cathepsin F mRNA is more highly expressed in N9 cells and lung (Lu) compared with neonatal microglia, thymocytes (Thy), and splenocytes.