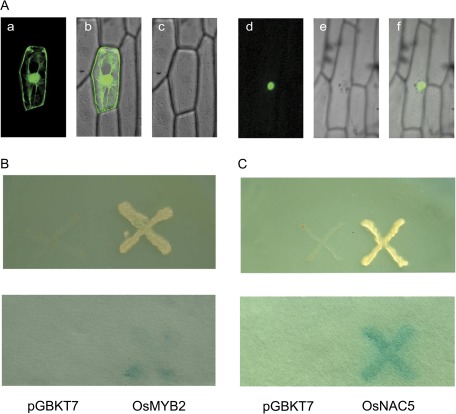
Fig. 1.
Subcellular localization and transactivation analysis of OsMYB2. (A) Nuclear localization of OsMYB2. Confocal images of onion epidermis cells under the GFP channel showing the constitutive localization of GFP (a) and nuclear localization of OsMYB2-GFP (d). The confocal images (b and e) are of the same cells in (a) and (d) with transmitted light. The merged images (c and f) are of (a) and (b) and (d) and (e), respectively. GFP or OsMYB2-GFP fusion was driven by the control of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Onion epidermal peels were bombarded with DNA-coated gold particles and GFP expression was visualized 24 h later. (B) Transactivation assay of OsMYB2 in the yeast strain AH109. Fusion protein of the GAL4 DNA-binding domain and OsMYB2 were expressed in yeast strain AH109. The vector pGBKT7 was expressed in yeast as a control. The culture solution of the transformed yeast was dropped onto SD plates without tryptophan, histidine, or adenine. The plates were incubated for 3 days (upper) and then subjected to β-galactosidase assay (lower). (C) Transactivation assay of OsNAC5 in the yeast strain AH109.