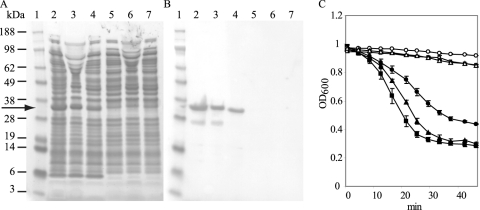
Fig 3.
Activity of CS74L in crude protein extracts. (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of crude extracts from E. coli expressing His-tagged endolysin CS74L or empty vector controls. Lane 1, SeeBlue marker (Invitrogen); lanes 2 to 4, E. coli cs74l-pET15b total protein; lanes 5 to 7, E. coli pET15b total protein. Proteins were tested after 4 h induction with IPTG, extracted with 20 mM sodium phosphate (pH 6) (lanes 2 and 5), 100 mM HEPES (pH 7) (lanes 3 and 6), or 20 mM Tris HCl, 50 mM NaCl (pH 8) (lanes 4 and 7). Crude protein samples were loaded at 10 μg per lane. The arrow indicates endolysin CS74L. (B) Western blot analysis of the gel in panel A hybridized to His tag antibody. (C) Turbidity reduction assay of frozen cells of C. sporogenes 17886 incubated with 10 μg crude protein extracts from E. coli expressing cs74l-pET15b (filled symbols) or pET15b (open symbols) extracted in 20 mM sodium phosphate (pH 6) (■), 100 mM HEPES (pH 7) (●), or 20 mM Tris HCl, 50 mM NaCl (pH 8) (▲). Values are means from replicate assays ± standard deviations.