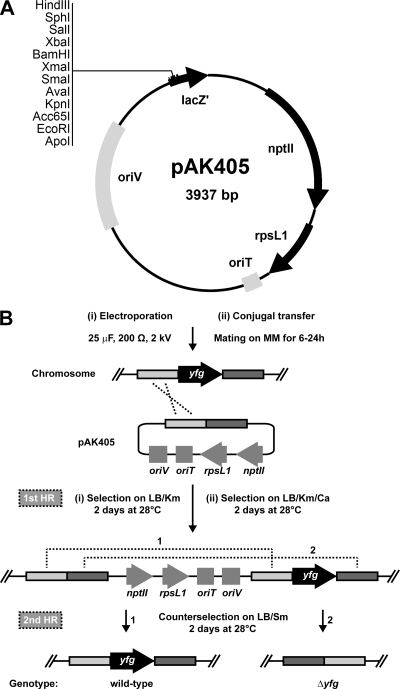
Fig 3.
pAK405 plasmid map and schematic of the gene deletion strategy. (A) Plasmid pAK405 has the following features: a pBR322 oriV (suicide plasmid for Sphingomonas), the RP4 oriT (for conjugal transfer between E. coli and Sphingomonas), the pUC18 multiple cloning site in lacZ′ (allowing blue/white screening), nptII (for selection on kanamycin), and rpsL1 (for streptomycin counterselection). Unique restriction sites in the multiple cloning site are shown. (B) Outline of the gene deletion strategy with delivery of pAK405 through electroporation (i) or conjugal transfer (ii). The gene of interest (yfg, “your favorite gene”) to be deleted is shown as a black arrow, and up- and downstream regions are depicted in light and dark gray boxes, respectively. Homologous recombination (HR) events are represented by dashed lines. For simplicity, only one of two possibilities for the first HR event is shown (HR via the upstream region). For the second HR event, the two possibilities leading to the wild-type (1) and mutant (2) genotypes are depicted. Antibiotics are indicated as follows: Km, 50 μg kanamycin/ml; Ca, 50 μg carbenicillin/ml; Sm, 100 μg streptomycin/ml.