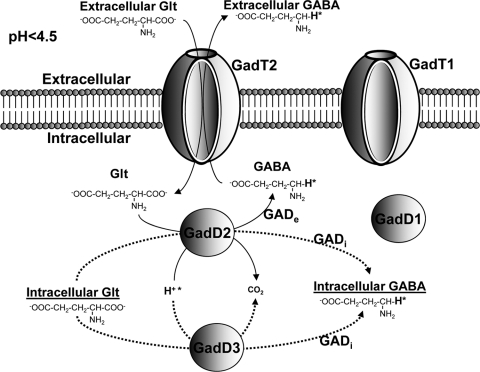
Fig 1.
Model for the function of the GAD system under severe acid conditions (pH < 4.5). The GadT2 antiporter imports extracellular Glt, which is decarboxylated by GadD2 to GABA with the concurrent consumption of a proton (H+*). GABA is then exported by the GadT2 with the simultaneous import of Glt. The above-described process is carried out by the GADe, which is depicted by bold lines. Intracellular Glt is decarboxylated by GadD3 and GadD2, resulting in the accumulation of GABAi. The latter process is carried out by GADi, which is depicted by dotted lines. The contribution of GadD1 and GadT1 in both the GADe and GADi processes is minor according to the results presented here. GadD3 has previously been suggested by various authors to be a Glt decarboxylase, but further work is required to prove this.