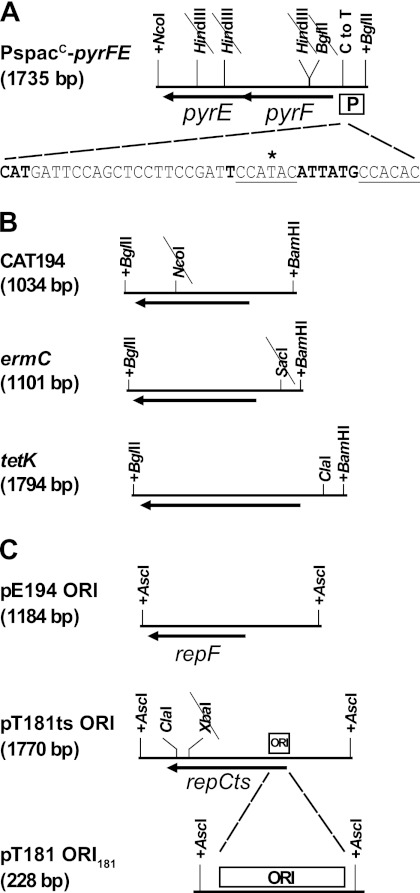
Fig 2.
Cassettes used in vector construction. Added restriction sites are indicated by a plus sign before the restriction site, whereas a slash through the restriction site indicates that the restriction site was removed by a silent point mutation. The two ClaI sites used for the deletion in pRLYT8 are indicated. (A) The PspacC-pyrFE cassette, with pyrF and pyrE genes from B. subtilis. The C-to-T point mutation used to avoid instability in E. coli is indicated. The −10 box, the transcription start site, and the start codon are indicated in bold type. The 6-bp repeats are underlined, and the asterisk indicates where we introduced the C-to-T point mutation. The three HindIII sites and a BglII site were removed from the pyrFE genes by site-directed mutagenesis to maintain the uniqueness of the corresponding sites. (B) Antibiotic resistance cassettes used for construction of the pRLYx1 vectors. An NcoI site in CAT194 and a SacI site in ermC were removed by site-directed mutagenesis via silent mutations. (C) Origins of replication used for construction of the pRLYx2, pRLYx8, and pRLYx9 vectors. ORI181 (ORI) is indicated, and broken lines indicate the section of the full-length pT181ts origin of replication, which comprises the ORI181, used for the pRLYx2 vectors. The XbaI site was mutated in the pT181ts origin.