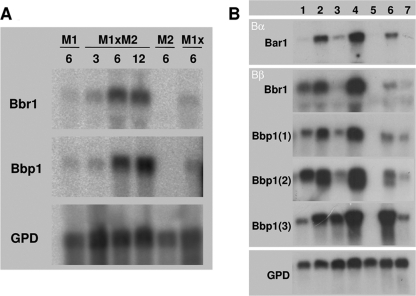
Fig 4.
Northern hybridization of receptor and pheromone gene expression during compatible and semicompatible matings. (A) Expression of the Bbr1 receptor and the Bbp1 pheromone-encoding genes in a compatible mating, 4-40 (M1; A4,6;B1,1) × 4-39 (M2; A1,1;B3,2), and the two respective monokaryons, as well as an incompatible cross between identical monokaryons (M1x). RNA extraction was performed after the indicated times (3, 6, 12 h). (B) Expression of the receptor genes encoding Bar1 and BbrI and also those encoding the pheromones Bbp1(1), Bbp1(2), and Bbp1(3). Lane 1, expression in Aon semicompatible mating between strains 23 (A4,6;B3,1) × 684 (A2,6;B3,1); no signal was expected for bar1 since neither of the B loci encodes the bar1 receptor; lanes 2 and 3, Bon semicompatible matings between strains 1792-114-10 (A4,6;B3,6) × 4-40 (A4,6;B1,1) and 43/26 (A4,6;B3,1) × 4-40 (A4,6;B1,1), respectively; lane 4, Aon;Bon fully compatible mating between strains 4-40 (A4,6;B1,1) × 4-39 (A1,1;B3,2); lane 5, strain 4-39 (A1,1;B3,2); no signal was expected in this control since no sequences encoding either the Bar1 and Bbr1 receptor or any of the three Bbp1 pheromones are present in strain 4-39; lane 6, strain 4-40 (A4,6;B1,1); lane 7, strain 23 (A4,6;B3,1). All strains were grown for 8 h after mating. Each well contains 20 μg of total RNA. Expression of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) was monitored as a loading control.