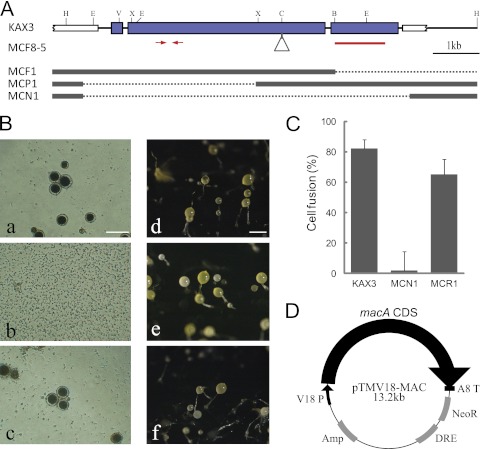
Fig 1.
Generation of sexually defective mutants. (A) The genomic structure of the macA region for the parental KAX3 strain is shown on top. The thick blue and white bars indicate the exon of macA and neighboring genes, respectively. The triangle shows the vector insertion site in MCF8-5. For the other 3 mutants, substitutions to the vector sequences are shown by dotted lines. Red bars and arrows indicate the region used for the hybridization probe and the quantitative RT-PCR primers, respectively. Restriction sites are the following: B, BamHI; C, ClaI; E, EcoRI; H, HpaI; V, EcoRV; and X, XbaI. (B) Macrocyst (a, b, and c) and fruiting body formation (d, e, and f) of parental KAX3 (a and d), the macA-null mutant MCN1 (b and e), and the macA overexpression mutant in MCN1, MCR1 (c and f). For macrocyst formation, 100 cells were mixed with an equal number of V12 cells in 100 μl of BSS containing condensed K. aerogenes in a well of a 96-well plate and cultured for 4 days at 22°C. Bar, 100 μm. (C) Results of the cell fusion assays are shown. (D) Structure of the macA overexpression vector. The coding sequence of macA was inserted between the V18 promoter and the act8 terminator of pTMV18.