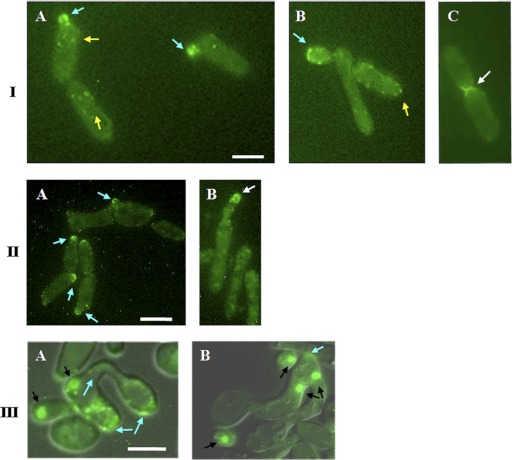
Fig 1.
Localization of Myo5p-GFP in opaque C. albicans cells at different stages of the cell cycle and development. (I) (A and B) Myo5p-GFP is localized in cortical patches in MTLa/MTLa MYO5/MYO5-GFP mother cells (yellow arrows) and at the tips of emerging buds (blue arrows). (B) Subsequently, Myo5 redistributes evenly in an isotropic growing bud and then moves to the bud tip (blue arrow). (C) After nuclear division, Myo5p-GFP localization is observed at the mother-bud neck (white arrow). Bar, 3 μm. (II) Myo5p-GFP localizes in patches at the shmoo tips. C. albicans shmoos (blue arrows) (A) keep growing after emergence and continue to accumulate Myo5p at the shmoo apexes (white arrows) (B). Bar, 3 μm. (III) Mating between MTLa/MTLa NOP1/NOP1-YFP MYO5/MYO5-GFP and MTLα/MTLα MYO5/MYO5-GFP strains. (A) Myo5p patches (arrows) localize randomly in parent cells and in the conjugation bridge. (B) Concentration of Myo5p (arrows) at the site of first daughter cell formation. A mating mixture of the MTLa NOP1/NOP1-YFP MYO5/MYO5-GFP and MTLα MYO5/MYO5-GFP strains was cultivated O/N on solid Spider medium at 24°C. Black arrows point to the Nop1-GFP signal. Fluorescent images of Myo5p and Nop1p are superimposed on differential interference contrast images. Bar, 5 μm.