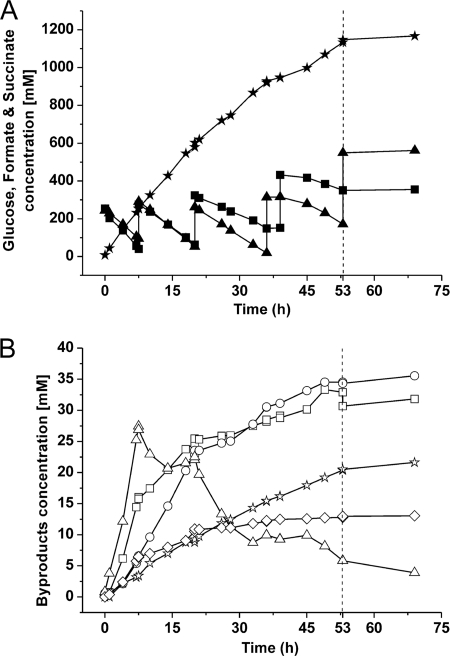
Fig 4.
Representative anaerobic fed-batch fermentation with C. glutamicum strain BOL-3/pAN6-gap showing succinate production (black stars) during coutilization of glucose (black squares) and formate (black triangles) (A) and formation of the by-products pyruvate (open triangles), acetate (open stars), α-ketoglutarate (open circles), malate (open squares), and fumarate (open diamonds) (B). The dashed line shown after 53 h of incubation marks the end of anaerobic succinate production activity. The experiment was performed in a Multifors bioreactor system, and the cells, pregrown aerobically, were resuspended in 450 ml of a solution containing 0.9% (wt/vol) NaCl, 220 mM glucose, 250 mM NaHCO3, and 220 mM sodium formate. The cell suspension had an initial OD600 of about 50. After 7.5, 20, and 39 h, 222 mM glucose and 250 mM NaHCO3 were added. After 7.5 and 20 h, 200 mM sodium formate was added, and after 36 and 53 h, 290 mM sodium formate was added. The pH was kept at pH 6.9 by automated addition of 4 M KOH. After feeding with NaHCO3, the pH increased to between 7.2 and 7.4 and then returned to pH 6.9 by the acid production of the cells. Two independent fermentations were performed, with both showing comparable results with respect to product yield (5% difference) and titer (10% difference).