Fig 2.
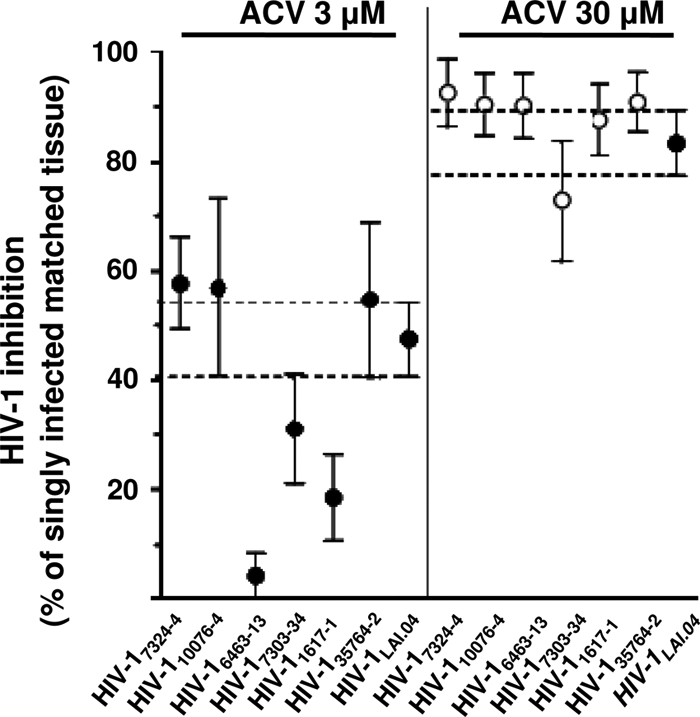
Inhibition of replication of multidrug-resistant HIV-1 clones by ACV in human lymphoid tissues. Donor-matched sets of tissue (27 blocks for each experimental condition from each of three to seven donors) were incubated with ACV (3 or 30 μM) for 12 days or used as untreated controls. Some of these sets were infected with multi-NRTI-resistant clones HIV-17324–4, HIV-110076–4, HIV-17303–3, HIV-16463–13, HIV-11617–1, and HIV-135764–2 or with the laboratory strain HIV-1LAI.04. Replication of HIV-1 was evaluated by p24gag core antigen release in pooled medium bathing 27 tissue blocks using a bead-based assay. The anti-HIV activity of ACV, as a percentage, was evaluated by comparing viral replication in drug-treated tissues with that in untreated donor-matched control tissues. Presented are means ± SEM of HIV-1 inhibition in 27 human tissue blocks from each of three to seven donors, relative to results for matched untreated tissues (n = 3 for HIV-17324–4 and HIV-16463–13; n = 4 for HIV-11617–1; n = 7 for HIV-110076–4, HIV-17303–3, HIV-135764–2, and HIV-1LAI.04).
