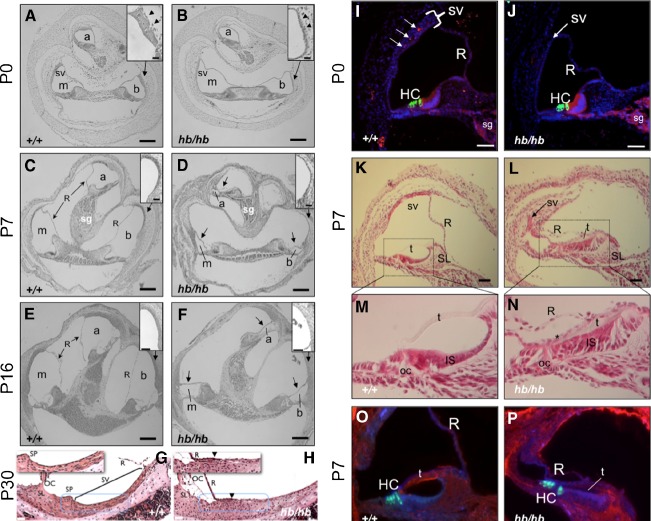
FIG. 3.
Defects in the stria and altered differentiation in the cochlea of head bobber ears. Transverse sections of inner ears are shown from P0 (A–B; I–J), P7 (C–D; K–P), P16 (E–F), and P30 (G–H), +/+ (A–O) and hb/hb (B–P). hb/hb have defects in the scala media. Sections through the cochlea show a poorly developed stria vascularis (sv, compare arrowheads in A and B insets) in hb/hb at P0. The scala media is further compromised by a collapse of Reissner’s membrane (R), shown at P7 (arrows in D) and P16 (arrows in F). The stria vascularis has completely lost the multilayer structure and appearing flat with reduced capillaries (compare insets in C to D and panels G to H). Moreover, blood vessels are readily visualized in wild-type (I) but severely reduced in the stria (sv) of hb/hb ears (J) as detected by anti-cadherin immunostaining (red) at P0. The stria in hb/hb (arrow in J) is significantly thinned compared with the DAPI-stained nuclei in the wild-type (bracketed in I). In the organ of Corti (oc), hb/hb hair cells (HC) and spiral ganglion (SG) express appropriate differentiation markers; compare myosin VII (green) and cadherin (red) in J to I. At P7, the hb/hb stria (arrow in L) is a remnant compared with the wild-type (K) stria at the apical turn and Reissner’s (R), and tectorial (t) membranes are collapsed onto the poorly differentiated inner sulcus (IS) (compare K to L, M to N and O to P). There also is a reduced expression of fibronectin (blue) in the hb/hb tectorial membrane (compare t in P to O). a, apical scala; b, basal scala; m, media scala; sg, spiral ganglion. GSLI lectin (red); SL, spiral limbus, SP, spiral prominence. Scale bar = 100 μm (A–F); 20 μm (insets in A, B; C, D; E, F, and in panels G–H); or 50 μm (I–P).