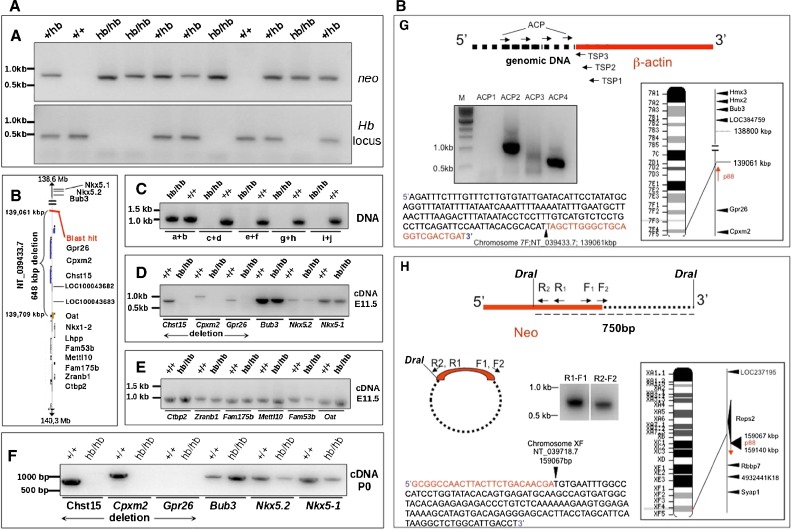
FIG. 5.
Head bobber genotyping, delineation of the deleted portion of chromosome 7, and identification of the transgene integration site. A PCR genotyping using Neo (top) and chromosome 7 (bottom) primer sets in +/+, hemizygous (+/hb), and head bobber (hb/hb) mice. B Haplotype diagram of the head bobber locus on chromosome 7 and gene loci interrogated by PCR analysis (C) for the extent of genomic deletion surrounding the hb locus (primers a–i are listed in Table I). Blast hit in B, initial sequence comparison location. D–F RT-PCR analyses for gene expression (primers are listed in Table II) in the head bobber region at E11.5 (D, E) and at P0 (F) from +/+ and head bobber (hb/hb) inner ears. G Using specific primers (TSP1, TSP2, TSP3, top panel) designed to the β-actin region and DNA Walking primers (top panel, ACP; designed to capture transgene flanking genomic sequences) specific bands were amplified (bottom panel) that were mapped to sequences on chromosome 7 (right panel). H Inverse PCR of DraI digested hb/hb genomic DNA (top panel) was circularized (middle panel), and nested primers (reverse R1, R2, and forward F1, F2) designed in the Neo gene were used to perform primary (R1–F1) and secondary (R2–F2) inverse PCR resulting in a approx. 750 bp band (bottom panel) that was mapped to chromosome X. Sequencing of cloned fragments allowed orientation of the transgene in the genome (arrows in chromosome maps).