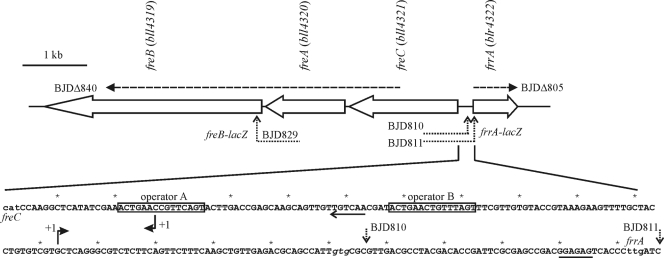
Fig 1.
The frrA-freCAB gene region and its putative regulatory elements. In the upper section, open arrows symbolize orientations and sizes of genes. Dashed horizontal lines indicate the deleted region in the listed mutant strain. The arrowheads show the orientation of the kanamycin resistance marker. Dotted bent arrows mark the positions of putative translational lacZ fusions within frrA or freB. The horizontal part of these arrows depicts the region used for homologous recombination and integration of the reporter gene. In the lower section, the translational start codons of freC and frrA are indicated at the ends of the nucleotide sequence in lowercase letters. The annotated start codon of frrA (gtg), which is located 48 nt upstream of the experimentally determined start codon, is shown in italics. Dotted vertical arrows denote the integration sites of the lacZ reporter within the frrA open reading frame. A Shine-Dalgarno-like sequence upstream of the identified start codon of frrA is underlined. Bent arrows (+1) indicate transcriptional start sites and directions. Palindromic sequences are boxed. A horizontal arrow marks a potential −35 promoter element.