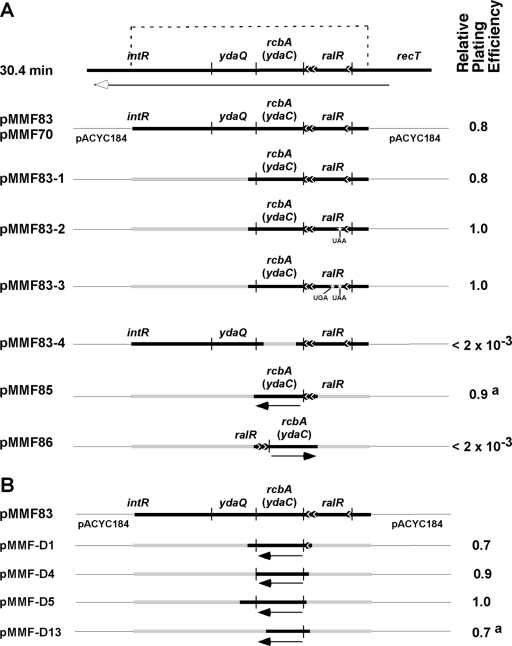
Fig 1.
Deletion analysis and the multicopy suppressor assay identifies rcbA (née ydaC) as a suppressor of lethality caused by overinitiation. The thick and thin horizontal lines represent E. coli DNA and pACYC184, respectively. Vertical lines denote the approximate boundaries of each gene. The shaded thick lines symbolize DNA that has been deleted. The filled circles with arrows represent putative promoters for rcbA, named rcbAp3 at −12 to −28 bp, rcbAp2 at −35 to −63 bp, and rcbAp1 at −151 to −182 bp upstream from rcbA. In the column at the right, the relative plating efficiency was measured by a multicopy suppressor assay with E. coli XL1-Blue (relevant genotype, recA1) cells that were coelectroporated with the dnaA expression plasmid (pDS596) and the indicated plasmid (see Materials and Methods). (A) Genes at 30.4 min of the E. coli chromosome. The line with the arrowhead indicates the polarity of transcription, and the bracket represents the 1,301-bp DNA fragment inserted into the BamHI site of pACYC184 in two independently obtained isolates (pMMF83 and pMMF70). The inserted genes that include part of intR and recT have the same polarity as the tetracycline resistance gene of pACYC184. The construction of other plasmids is described in Materials and Methods. (B) The inserted DNA fragment in pMMF83 was PCR amplified and digested with DNase I in the presence of a manganese ion, and the blunt-end fragments were inserted into the EcoRV site of pACYC184. Fragments inserted into pMMF-D1, pMMF-D4, pMMF-D5, and pMMF-D13 start at 42, 23, 11, and 33 bp upstream of rcbA, respectively, and are oriented with the same polarity as the tetracycline resistance gene of pACYC184. The DNA fragments in pMMF-D1 and pMMF-D5 extend 30 and 60 bp beyond the stop codon of rcbA, respectively. The inserted DNA in pMMF-D4 ends at the stop codon of rcbA, whereas pMMF-D13 lacks 44 bp from the C-terminal coding region of rcbA and is in frame with the remainder of the tetracycline resistance gene. a, small colonies on arabinose-supplemented medium compared with the strain bearing pMMF83.