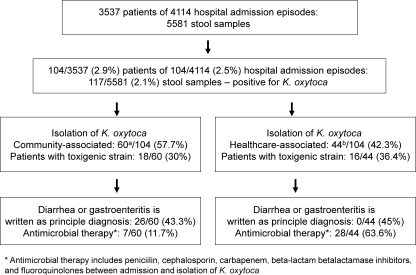
Fig 3.
Workup for Klebsiella oxytoca in a regional hospital in Hong Kong (1 November 2009 to 30 April 2011). a, 21/60 (35%) patients were coinfected with other pathogens, including 5/60 (8.3%) patients with other bacteria detected by culture (Salmonella spp. in 4 cases and Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni in 1 case); 8/60 (13.3%) patients with norovirus detected by RT-PCR, among whom were 2 patients from residential care homes; 3/60 (5%) patients with rotavirus detected by a latex agglutination test; 3/60 (5%) patients with toxigenic strains of Clostridium difficile detected by a cell culture assay; and 2/60 (3.3%) patients with both norovirus and toxigenic strains of C. difficile. b, 7/44 (15.9%) patients were coinfected with other pathogens, including 4/44 (9.1%) patients with a toxigenic strain of C. difficile detected by a cell culture assay, 2/44 (4.5%) patients with rotavirus detected by a latex agglutination test, and 1/44 (2.3%) patients with Aeromonas caviae detected by culture.