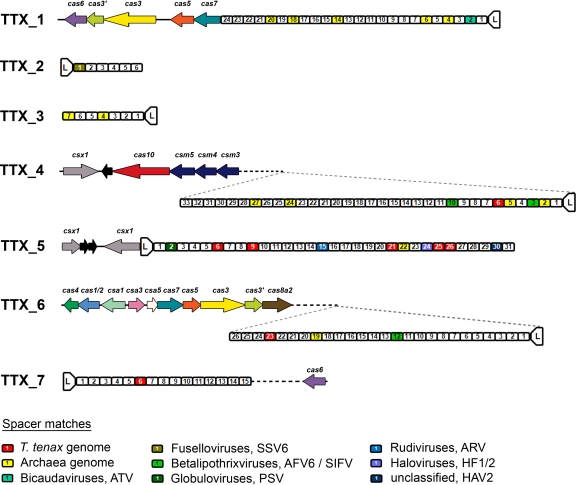
Fig 2.
CRISPR loci, spacer similarities and adjacent cas genes in T. tenax. Seven CRISPR loci (TTX_1 to TTX_7) were analyzed from the genome and spacers consecutively numbered (for example, spacer 1.1 is spacer 1 from TTX_1) starting from the localization of the leader sequence (L). All 142 spacer sequences were searched for sequence similarities and spacers with significant homology to archaeal viruses, Archaea, or T. tenax genes are indicated by colors. For every CRISPR loci the adjacent cas genes were identified by analyzing protein sequences by BLASTp and comparison to respective Pfam (19), TIGRFam (28), and COG numbers. CRISPR locus TTX_1 is surrounded by a subset of core cas genes (ORFs, TTX_0232 to TTX_0235). At locus TTX_4 the csm gene cluster (csx1, cas10, and csm3 to csm5, subtype III-A; ORFs, TTX_1228 to TTX_1233) is located and, in addition, at locus TTX_5 (ORFs, TTX_1240 and TTX_1243) two genes with homology to csx1 were identified. The specific genes for subtype I-A can be found at TTX_6 with two clusters (cas4, cas1/2, and csa1 and csa5, cas7, cas5, cas3, cas3′, and cas8a2, subtype I-A; ORFs, TTX_1245 to TTX_1255) and a potential regulator csa3 (ORF, TTX_1249) in between. A second cas6 (ORF, TTX_1272) gene is located near to TTX_7. Identical genes were marked by the same colors.