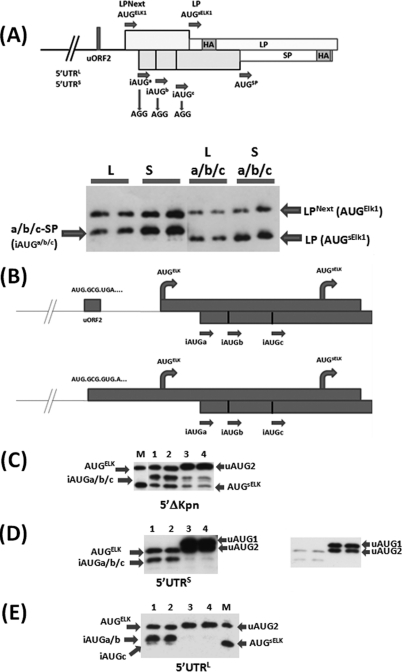
Fig 5.
The iAUGs serve to limit ribosomal access to the AUGsELK-1. (A) (Top) LP/SP reporter system that was adapted to monitor initiation events at the AUGELK-1, AUGsELK-1, and iAUG start codons. The position of the HA epitope in each ORF is indicated, as are the mutations introduced to remove the iAUG codons. The bars above and below the line indicate that LP and SP are in different ORFs. (Bottom) Immunoblot performed with the anti-HA antibody. HEK293T cells were transfected with the 5′ UTRL-LPNext (L), 5′ UTRS-LPNext (S), and the same 5′ UTRs carrying the iAUG → AGG changes (La/b/c and Sa/b/c). Transfections were performed in duplicate. (B) Schematic representation of the single nucleotide insertion within the uORF2 that fuses this ORF to the ORFs of AUGELK-1 and AUGsELK-1 (the LP ORF in the reporter). (C to E) Immunoblots performed with the anti-HA antibody for the three constructs tested. Lanes 1 and 2, WT constructs; lanes 3 and 4, iAUGa/b/c → AGG mutations. All clones were transfected in duplicate. The inset in panel D is a shorter exposure that demonstrates initiation products from both uAUG1 and uAUG2 (which are in the same ORF [Fig. 1A]). Lane M, a marker (the Sa/b/c construct depicted in panel A) for initiation products from the AUGELK-1 (LPNext) and AUGsELK-1 (LP).