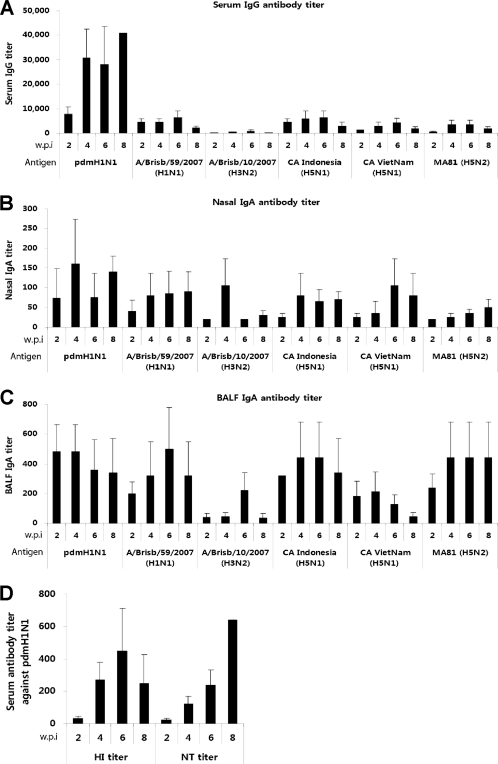
Fig 1.
Cross-reactive systemic and mucosal antibody responses to seasonal and H5 influenza viruses. To collect serum samples, eight 6-week-old female BALB/c mice were divided into two groups; the mice in one of the groups were immunized with one dose of 105 PFU of CApH1N1, and the mice in the other group received PBS as a control. Every 2 weeks, serum samples were collected from each of the eight mice. For bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF) and nasal wash sampling, 32 mice were divided into two groups, one for immunization with one dose of 105 PFU of CApH1N1 and the other for treatment with PBS as a control. Every 2 weeks, eight mice from the two groups were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and the BALF and nasal washes were harvested in PBS. The virus-specific IgG or IgA antibody titers were analyzed by ELISA. (A to C) Titers of serum IgG (A), nasal wash IgA (B), and BALF IgA (C) against six viruses are shown. Antibody titers are expressed as the reciprocal of the dilution that yielded an optical density above the mean plus two times the standard deviation (SD) of PBS control sample results. (D) With the same serum samples, the hemagglutinin inhibition (HI) antibody titers and viral neutralization (NT) antibody titers against homologous vaccine strain were also estimated. None of the PBS groups produced a detectable level of antibody titer. Data represent the means of the results determined for each cohort (n = 4), and error bars indicate ±SD. Detection limits were 160 for serum IgG titer, 20 for IgA titer, 8 for HI antibody titer, and 20 for NT antibody titer. w.p.i, weeks postimmunization. pdmH1N1, 2009 pandemic H1N1 ca vaccine (CApH1N1). All experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Yonsei Laboratory Animal Research Center (YLARC).