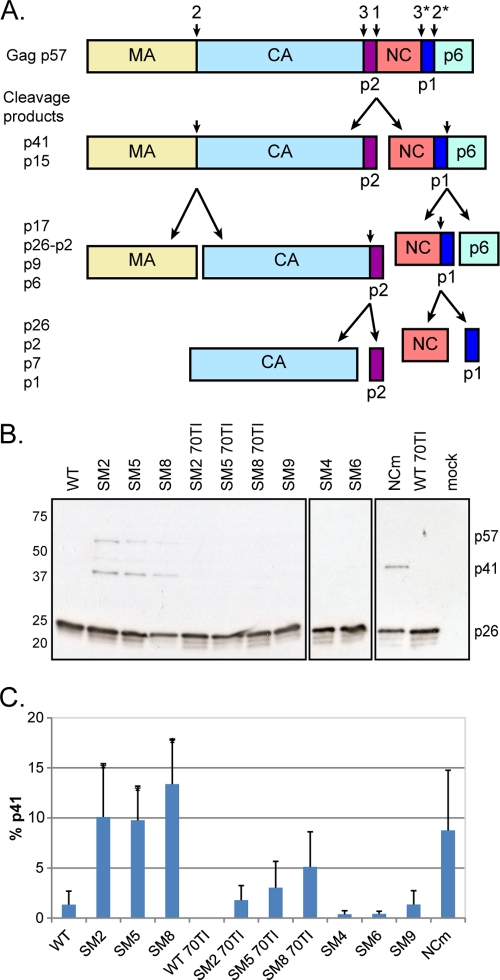
Fig 4.
Mutations affecting RNA dimerization and Gag-RNA interaction result in suboptimal processing and the accumulation of the p41 intermediate. (A) Schematic of the Gag polyprotein (p57) and its proteolytic processing. The sites and order of cleavage are indicated above the p57 precursor and each intermediate product. p17, matrix (MA); p26, capsid (CA); p2, spacer peptide p2, or SP1; p7, nucleocapsid (NC); p1, spacer peptide p1, or SP2; p41, MA-CA-p2; p15, NC-p1-p6; p9, NC-p1. (B) Western blot analysis of virion proteins, extracted at 48 h posttransfection, by use of an anti-SIVp57/27 antibody. The positions of Gag (p57), MA-CA-p2 (p41), and CA (p26) are indicated on the right. WT, wild type; 70TI, mutation in matrix at position 70; NCm, mutation of all Cys and His residues to Ala in the two NC zinc fingers. (C) Quantification of the percentage of the p41 cleavage intermediate in the virion (means + standard deviations) (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the wild type (*, P < 0.05) by the unpaired Student t test.