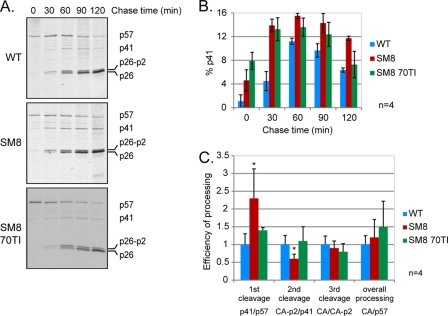
Fig 5.
The rate of Gag processing is altered in a replication-incompetent SL-1 mutant with impaired RNA dimerization. Pulse-chase metabolic labeling and immunoprecipitation of Gag were performed 24 h after transfection of C33-A cells with the WT, SM8, and SM8 MA 70TI proviral plasmids. Cells were starved of methionine (Met) and cysteine (Cys) for 60 min, pulse-labeled with [35S]Met-Cys for 30 min, and chased in cold medium for 30 to 120 min. Capsid-containing Gag proteins were immunoprecipitated from the culture supernatant at each time point with anti-SIVp57/p27, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography, prior to quantification by densitometry. (A) Representative results of pulse-chase metabolic labeling, immunoprecipitation, and gel electrophoresis are shown for each virus. The chase times are given above the gel, and the positions of Gag (p57) and its cleavage products MA-CA-p2 (p41), CA-p2 (p26-p2), and CA (p26) are indicated on the right. (B) Quantification of the percentage of the p41 cleavage intermediate for each virus (means ± standard deviations) (n = 4). (C) Efficiency of processing at 120 min postlabeling for each cleavage of Gag, as diagramed in Fig. 4A, corresponding to the ratio of the cleaved to the uncleaved product. Means + standard deviations are shown (n = 4). Asterisks indicate significant differences from the WT (*, P < 0.05) by an unpaired Student t test.