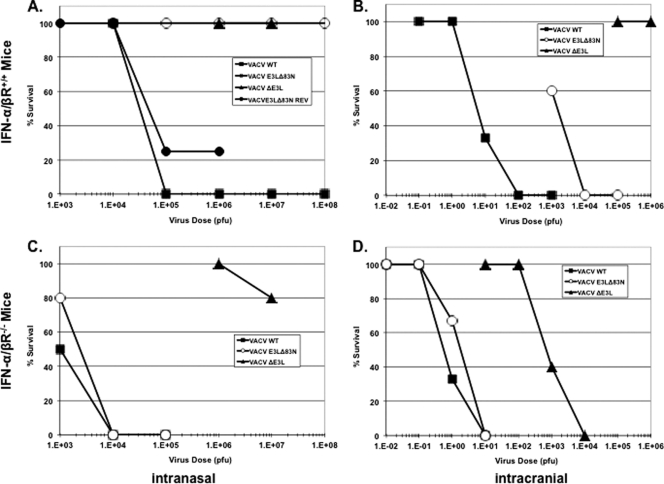
Fig 1.
Comparison of pathogenicity between IFN-α/βR+/+ and IFN-α/βR−/− mice infected intranasally (A and C) or intracranially (B and D) with VACV expressing E3L mutants. Four- to six-week old mice were infected intranasally or intracranially with increasing doses of wtVACV (squares), VACVE3LΔ83N (circles), or VACVΔE3L (triangles). Mice were weighed every other day, and the progression of disease was monitored. Mice dropping 30% of their initial weight were euthanized and considered dead (n = 5). WT, wild type.