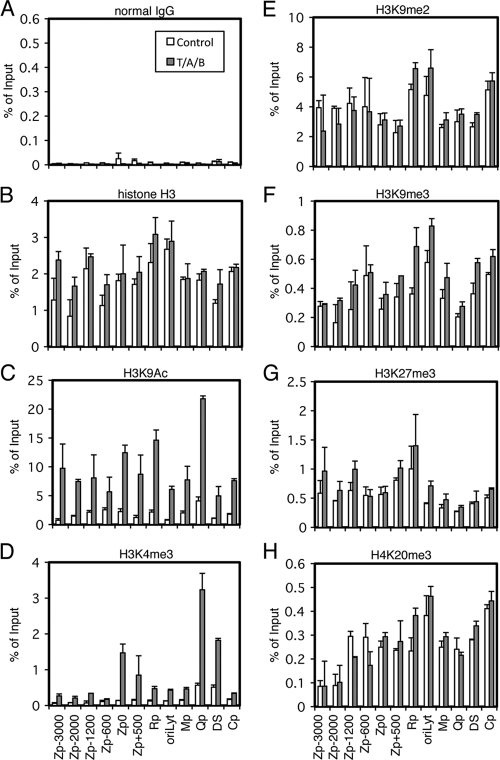
Fig 1.
Histone modification pattern of EBV Zp upon lytic reactivation. Raji cells were treated with TPA (20 ng/ml), A23187 (1 μM), and sodium butyrate (5 mM) (T/A/B; gray bar) or the vehicle (Control; white bar) for 20 h. Cells then were cross-linked, and ChIP experiments were performed as described in Materials and Methods using normal IgG (A), anti-histone H3 (B), anti-H3K9Ac (C), anti-H3K4me3 (D), anti-H3K9me2 (E), anti-H3K9me3 (F), anti-H3K27me3 (G), or anti-H4K20me3 (H) antibody, followed by DNA extraction and real-time PCR to detect DNA fragments using the primers as indicated. Zp, BZLF1 promoter; Rp, BRLF1 promoter; oriLyt, origin of lytic DNA replication; Mp, BMRF1 promoter; Qp, one of the EBNA promoters; DS, dyad symmetry, a part of oriP (origin of plasmid replication), containing multiple EBNA1 binding sites; Cp, one of the EBNA promoters. The number of Zp indicates sequence position relative to the transcription start site.