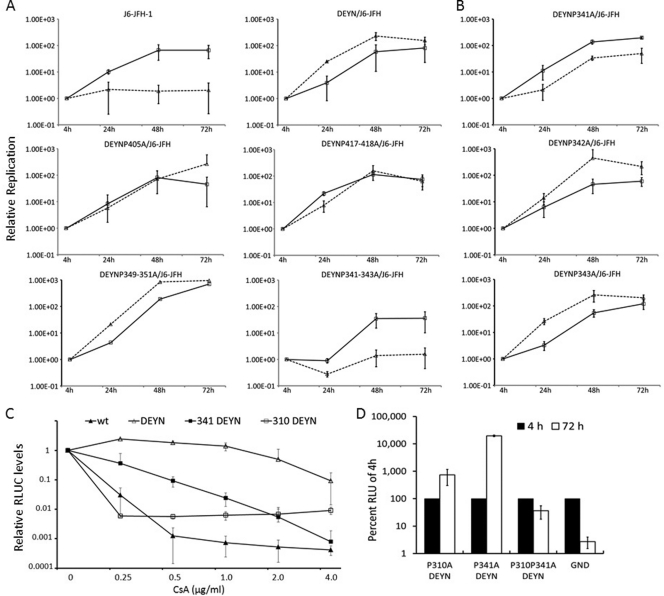
Fig 6.
Alanine scanning of NS5A LCS-II and domain III in the background of DEYN mutations identify P310 and P341 as important for CyPA dependence. Prolines from P341 to P446 were mutated in singlets, doublets, or triplets within the DEYN/J6-JFH construct. Mutant RNAs were electroporated into Huh-7.5 sh-Luc and sh-A161 cell lines. Luciferase assays were performed 4, 24, 48, and 72 h after electroporation. Values were normalized to the 4-h reading in panels A, B, and D, and error bars represent standard deviations from two independent experiments. Solid lines, sh-Luc cells; dashed lines, sh-A161 cells. (A) Replication profiles of proline mutants of LCS-II and domain III. Top, the wt phenotype compared to the DEYN phenotype demonstrates rescue in the sh-A161 cell line; middle left, representative replication kinetics of single mutations (e.g., DEYN P405A); middle right, those of double mutations (e.g., DEYN P417-418A); bottom, those of triple mutations. Whereas the DEYN P349-351A mutant exhibited a phenotype similar to that of the DEYN virus, the DEYN P341-343A mutant uniquely abrogates the ability of DEYN mutations to rescue replication in the sh-A161 cell line (please see the summary of all mutants in Table 4). (B) The individual DEYN P341A, P342A, and P343A mutations highlight the importance of P341 in CyPA dependence. (C) P310A and P341A increase sensitivity to CsA treatment. J6-JFH RNAs with indicated mutations were electroporated into the Huh-7.5 sh-Luc cell line and treated with CsA 24 h after electroporation. Cells were collected 72 h after treatment and assayed for luciferase activity. Fold changes in response to treatment were normalized to no treatment (set at 1) and plotted. (D) DEYN mutations were unable to rescue the lethal phenotype of P310A P341A.