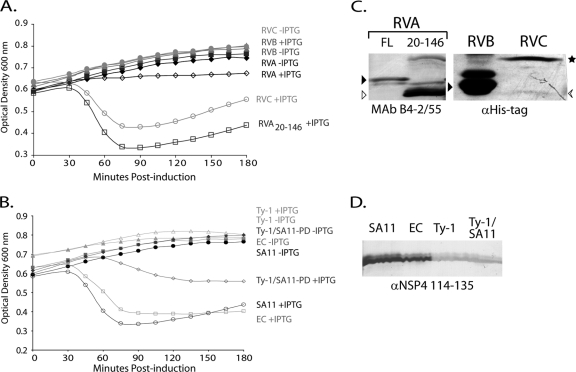
Fig 2.
NSP4 E. coli lysis activity is not conserved across rotavirus groups. (A) Full-length NSP4 from RVA, RVB, and RVC rotaviruses were tested for activity in an E. coli lysis assay. The optical densities at 600 nm of uninduced (closed symbols) or NSP4-expressing (open symbols) cultures were determined at 15-min intervals for 180 min. Black diamonds, RVA (SA11) NSP4; gray triangles, RVB (IDIR); light gray circles, RVC (Cowden); and dark gray squares, RVA aa 20-146 truncation. (B) E. coli lysis activity of SA11 NSP4 aa 20-146 (black circles) was compared to that of murine rotavirus EC (gray squares) and the avian rotavirus Ty-1 (light gray triangles). A chimeric Ty-1/SA11 construct was also tested (Ty-1/SA11-PD, dark gray diamonds) that replaced the Ty-1 NSP4 pentalysine domain (aa 47 to 72) with the SA11 NSP4 sequence. The optical densities at 600 nm of uninduced (closed symbols) and NSP4-expressing (open symbols) cultures were measured as described above. In all cases, the values are the mean from three independent experiments. (C and D) Immunoblots of NSP4 expressed in BL21(DE3)pLysS cells. (C, left) Full-length RVA NSP4 (FL; black arrowhead) and the aa 20-146 truncated NSP4 (white arrowhead) were detected with NSP4 MAb B4-2/55. (C, right) RVB (black arrowhead) and RVC NSP4 [arrow (monomer) and star (oligomer)] were detected anti-His-tag antisera. (D) NSP4s with aa 20-146 truncations from SA11, EC, and Ty-1 and the Ty-1/SA11 pentalysine domain (PD) chimera were detected with anti-NSP4 114-135 antisera.