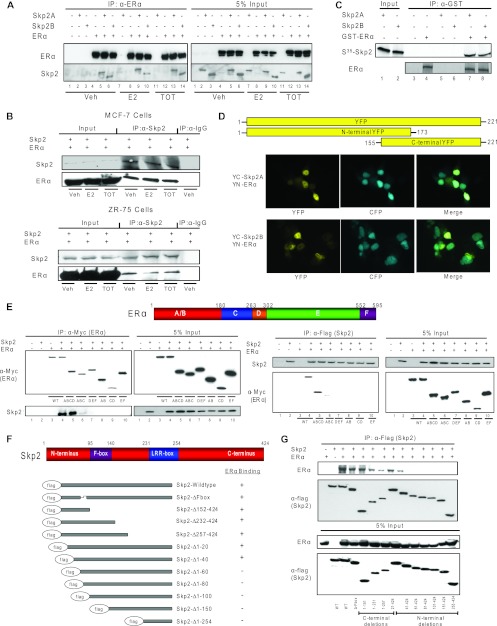
Fig 2.
Skp2 and ERα proteins interact in the cell nucleus through their N-terminal regions. (A) CoIP of Cos-1 cells treated with ligands for ERα and Skp2A or Skp2B. (B) CoIP of MCF-7 or ZR-75 cells treated with ligands for endogenous Skp2 and ERα. (C) In vitro GST pulldown assay. Shown is an immunoprecipitation of GST-tagged ERα in the presence or absence of in vitro-translated 35S-tagged Skp2. Coimmunoprecipitated Skp2 was analyzed by autoradiography. (D) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis. Cos-1 cells were transfected with YN-ERα along with YC-Skp2A or YC-Skp2B and CFP fused with the nuclear localization signal (to visualize cell nuclei), and YFP fluorescence was monitored by confocal microscopy. (E) CoIP of the ERα deletion mutant with Flag-Skp2 in Cos-1 cells. (F) Schematic of Skp2 deletion mutants showing their relative abilities to interact with ERα. (G) CoIP of the Skp2 deletion mutant with ERα in Cos-1 cells. All data are representative of 3 experiments.