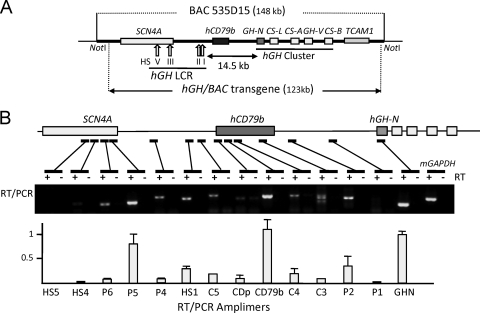
Fig 1.
Transcript mapping across the hGH/BAC transgene in the mouse pituitary revealed a peak of transcriptional activity across the hCD79b region. (A) Map of the hGH/BAC transgene. The 123-kb hGH/BAC transgene, released from the originating BAC clone by NotI digestion, was used to generate the hGH/BAC transgenic mouse lines (49). Each structural gene is indicated by a labeled box (exonic substructures are not shown). The vertical arrows labeled with roman numerals indicate the positions of DNase I hypersensitive sites (HS) that form in pituitary chromatin and constitute the hGH LCR. HSI,II are pituitary-specific DNase I HS of the hGH LCR. (B) Transcriptional profile across the hGH/BAC transgene. The presence of transcripts corresponding to each of 14 sites across the hGH/BAC transgene locus was determined by RT-PCR of transgenic mouse pituitary RNA. The position of each amplimer is indicated on the below the map by a bar and the sequences are listed on Table 1. Reactions were carried out in the presence or absence of reverse transcriptase (+ and −, respectively). Amplified cDNAs were analyzed on a 1% agarose gel. The concentration of each amplified RNA segment, shown in the histogram, was determined by PhosphorImager quantification of corresponding [α-32P]dCTP-labeled RT-PCR products generated by a separate set of reactions. Each value was normalized to a parallel amplification of genomic DNA to adjust for minor differences in amplification efficiency. The data are normalized to an arbitrary value of 1.0 for hGH-N mRNA. A robust transcriptional domain was detected over hCD79b, located between HSI and its target hGH-N.