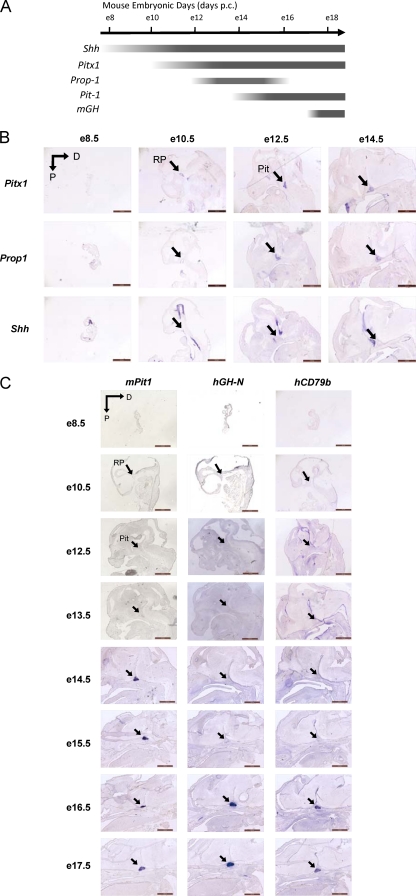
Fig 4.
Transcriptional activation of the hCD79b domain and activation of hGH-N expression are temporally concordant during pituitary development. (A) Timing of pituitary marker gene expression during mouse embryonic development. The approximate timing of mRNA expression of pituitary marker genes shown here is adapted and modified from Dattani and Preece (9). (B) Developmental time course of expression of Pitx1, Prop-1, and sonic hedgehog (Shh). In situ hybridization signals in the e8.5 through e14.5 mouse embryo heads of hGH/BAC (line BAC17) are shown. The transcription factor Pitx1 is an early pituitary-restricted maker initially expressed in Rathke's pouch at e9.5 (14, 52). This is followed by sequential activation of the genes encoding the transcription factors Prop-1 and Pit-1, at 12.5 and 13.5 dpc, respectively. Shh is expressed throughout the oral ectoderm except in the Rathke's pouch, creating a boundary between two ectodermal domains of Shh-expressing and -nonexpressing cells. Abbreviations: RP, Rathke's pouch; Pit, pituitary; D, dorsal; P, posterior. Scale bars, 1 mm. This study confirmed the embryonic dates of the samples as estimated from copulation timing. (C) Developmental time course of Pit1, hGH-N, and hCD79b. The transcriptional activation of Pit-1, hGH-N, and hCD79b was studied by in situ hybridization on hGH/BAC transgenic embryos (line BAC17) from e8.5 through e17.5, as indicated. Pit-1 mRNA signal was first detected at e14.5 (1). Its positioning is within the caudomedial region of the pituitary gland, a region that ultimately gives rise to somatotropes, lactotropes, and thyrotropes. Signals corresponding to hGH-N and hCD79b RNA first appear in the pituitary between e15.5 and e16.5. The timing of hGH-N activation was also assessed in (CDΔλ)hGH/BAC transgenic embryos; hGH-N mRNA was found to appear within the same time window and with the same pituitary-specific distribution as observed in the hGH/BAC embryos (data not shown).