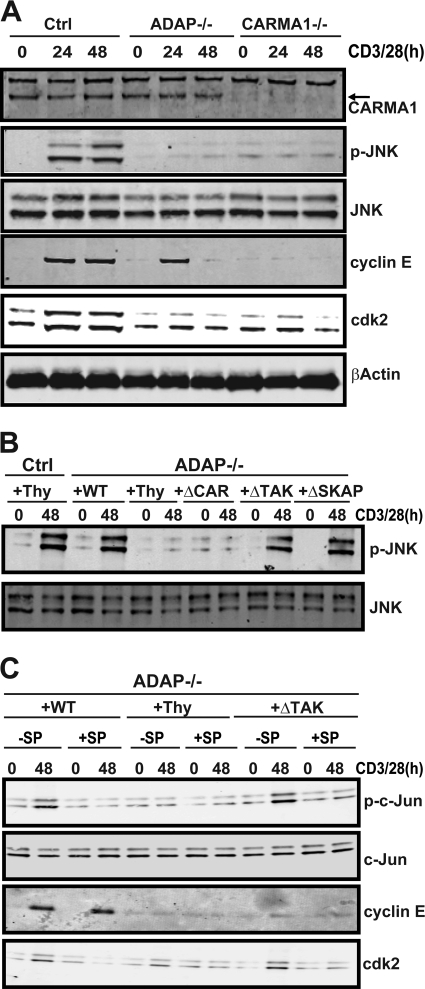
Fig 5.
The CARMA1-binding site in ADAP is critical for TCR-dependent JNK activation and induction of Cdk2. (A) Control (Ctrl), CARMA−/−, and ADAP−/− T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 48 h, lysed, and analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for JNK, phospho-JNK, cyclin E, Cdk2, and β-actin. (B) Naïve hCAR control or hCAR/ADAP−/− T cells were transduced with control adenovirus expressing Thy1.1 (Thy) or adenovirus expressing Thy1.1 and wild-type ADAP (WT), ADAPΔCAR mutant (ΔCAR), ADAPΔTAK mutant (ΔTAK), or ADAPΔSKAP mutant (ΔSKAP) and then stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies. Lysates were probed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-JNK (p-JNK) and anti-JNK antibodies. (C) Naïve hCAR control or hCAR/ADAP−/− T cells were transduced with the indicated adenoviruses as described for panel B and stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies for 48 h in the presence (+SP) or absence (−SP) of the JNK inhibitor SP6000125 (30 μM). Cells were harvested, lysed, and probed by Western blotting with anti-phospho-c-Jun, anti-c-Jun, anti-cyclin E, and anti-Cdk2 antibodies. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments.