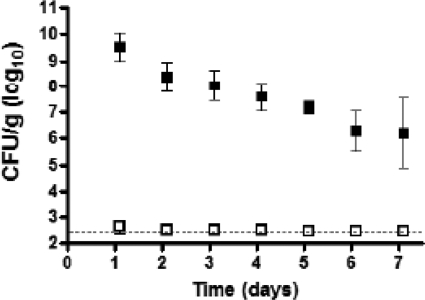
Fig 5.
Oral infection of mice with wild-type V. parahaemolyticus RIMD2210633 results in prolonged intestinal colonization and shedding in feces. Groups of C57BL/6 mice were orally dosed with PBS (open squares) (n = 5/group) or streptomycin (filled squares) (n = 6/group) 1 day prior to oral infection with V. parahaemolyticus. At the indicated intervals postinfection, fecal pellets were collected from mice, weighed, and homogenized in PBS. Samples were serially diluted and plated on LB agar containing 3% NaCl and 200 μg/ml streptomycin to determine the number of V. parahaemolyticus cells per gram of fecal material. The dotted line indicates the limit of detection for the assay. Error bars indicate ± standard deviations.