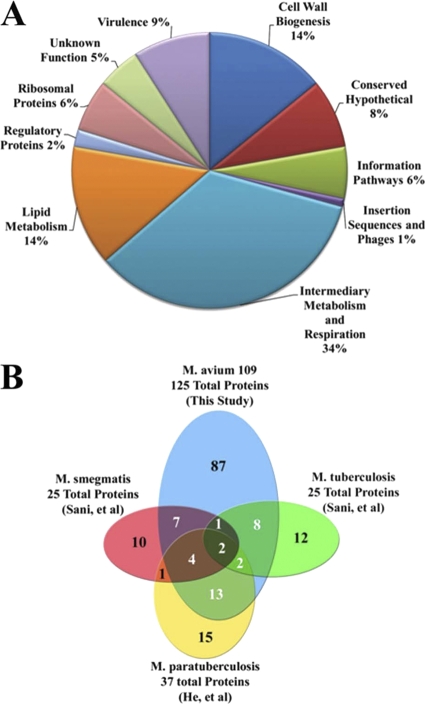
Fig 2.
Functional grouping and interstudy cross-referencing of identified surface-exposed proteins. (A) Distribution of functional annotations of identified M. avium subsp. hominissuis surface-exposed proteins. Direct homologues of all M. avium subsp. hominissuis proteins identified in this study were identified for M. tuberculosis, M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis, M. smegmatis, and M. marinum (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). Functional classification for identified M. avium subsp. hominissuis proteins was assigned, where applicable, by using the annotated functional grouping of the M. tuberculosis homolog in the Tuberculist database. (B) Venn diagram illustrating overlap between surface proteins identified in published studies of the surface-exposed proteomes of M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis, M. smegmatis, and M. tuberculosis and the data presented here for M. avium subsp. hominissuis. The data sets for M. smegmatis and M. tuberculosis employed selective solubilization to isolate surface proteins and included only the 25 most abundant surface proteins. The data for M. avium subsp. paratuberculosis employed a trypsin-shaving approach and included all confidently identified surface proteins (30–32, 51, 54, 74, 84).