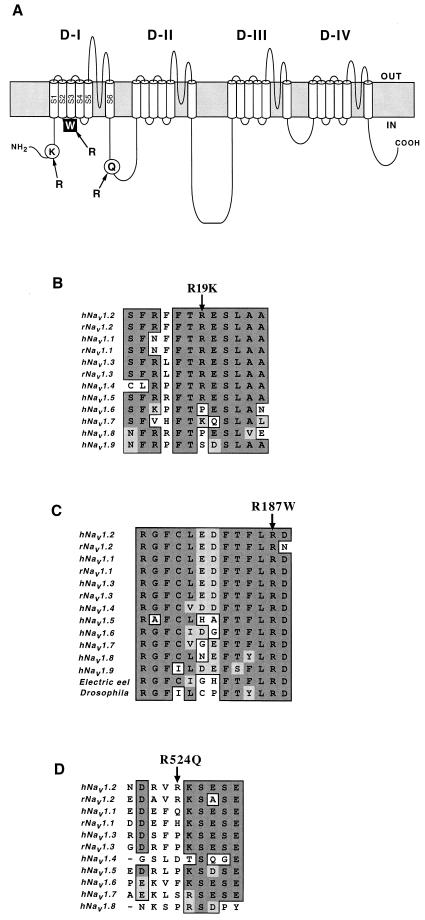
Figure 2.
Diagram of Nav1.2 and amino acid sequence alignments of Na+ channel α-subunit family members. (A) Locations of missense mutations identified in this study on Nav1.2. Filled square indicates the mutation proposed to be responsible for the disease phenotype. The amino acid exchanges indicated by open circles are ones assumed to be benign variants. (B–D) Partial amino acid sequences of Nav1.2 and other α-subunit family members (GenBank accession nos.: M94055, M22253, Y00766, M81758, M77235, AB027567, X82835, AF117907, AF188679, D37977, L19979, M22252, and M32078). Dark shaded background indicates identical amino acids, light shaded background indicates conserved amino acids, and white background depicts nonconserved amino acids. Arrows above the sequences indicate the positions of the missense mutations, R19K (B), R187W (C), and R524Q (D). Arg187 is highly conserved among the α-subunits of voltage-gated Na+ channels (C).