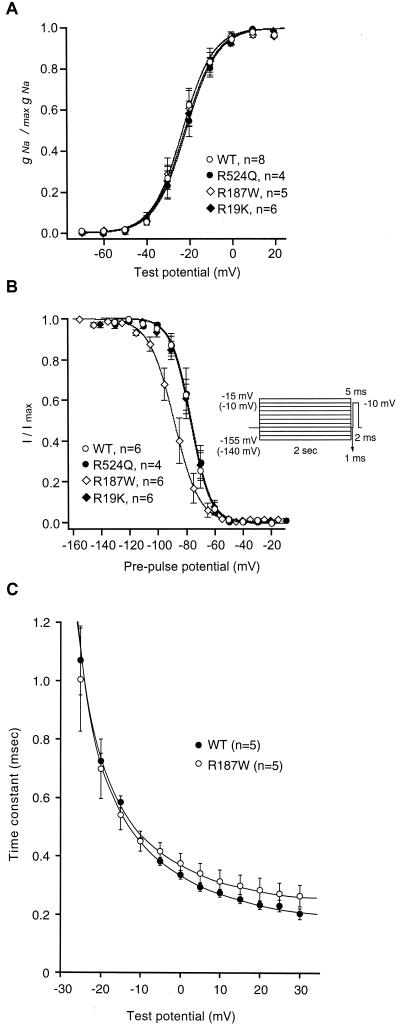
Figure 4.
Effects of missense mutations on conductance-voltage relationships and steady-state inactivation. (A) Peak conductance-voltage relationships for WT (open circle), R524Q (filled circle), R187W (open diamond), and R19K (filled diamond) Na+ channels expressed in HEK cells. No significant differences were detected between WT and mutant channels. Number of experiments was four, and all data were pooled. Curves are fitted to the data by using the equations given in Materials and Methods. (B) Steady-state voltage dependence of inactivation for WT (open circle), R524Q (filled circle), R187W (open diamond), and R19K (filled diamond) Na+ channels. Two different protocols were used. The prepulses were applied from −155 to −15 mV for WT, R524Q, and R19K mutant channels, and from −140 to −10 mV for R187W mutant channel with 10-mV increments. The half-inactivation potential and slope factors were estimated to be −76.9 mV and 6.7 for WT, −76.4 mV and 6.8 for R524Q, −88.6 mV and 8.7 for R187W, and −77.2 mV and 6.9 for R19K. All data were pooled and fitted as in A. (C) Voltage dependence of the inactivation time constant for WT and the R187W mutant channels. Note the clear difference in maximal rate of inactivation at the depolarized membrane potentials between WT and the R187W mutant.