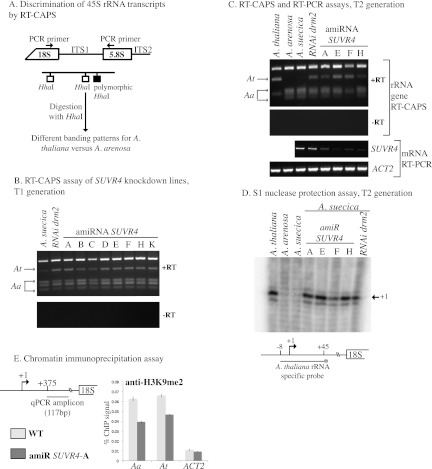
Figure 2.
SUVR4 is implicated in nucleolar dominance. (A). Diagram outlining the CAPS assay that distinguishes the A. arenosa- or A. thaliana-derived rRNA genes or their transcripts in A. suecica. (B) RT-CAPS analysis of rRNA gene variant expression in SUVR4 knockdown lines (T1 generation), nontransgenic A. suecica (negative control), or a DRM2 RNAi knockdown line (positive control). Control reactions in which reverse transcriptase was omitted (−RT) are also shown. (C) Persistence of disrupted nucleolar dominance in T2 siblings of a SUVR4 knockdown line. Also shown are SUV4 mRNA levels in the knockdown lines relative to A. suecica and DRM2-RNAi controls. RT–PCR of actin (ACT2) served as a control, showing that equivalent amounts of RNA were assayed. (D) S1 nuclease protection assay following hybridization of total RNA with an end-labeled A. thaliana-specific ssDNA probe. Following S1 nuclease digestion, products were subjected to denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography. (E) ChIP analysis of H3K9me2 levels in the region downstream from the transcription start site in wild-type A. suecica and SUVR4 amiRNA plants. Quantitative PCR used TaqMan probes. ACTIN2 served as a H3K9me2-depleted control.