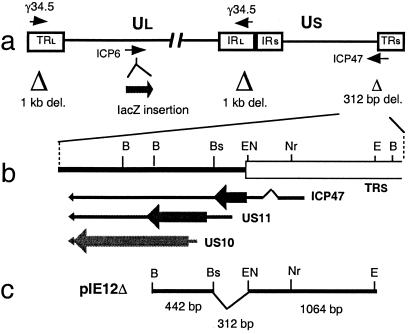
Figure 1.
Structure of G47Δ. (a) Schematic of the HSV-1 genome showing the regions modified in G47Δ. The HSV-1 genome consists of long and short unique regions (Ul and Us) each bounded by terminal (T) and internal (I) repeat regions (Rl and Rs). The parental virus G207 was engineered from wild-type HSV-1 strain F by deleting 1 kb within both copies of the γ34.5 gene and inserting the E. coli lacZ gene into the ICP6 coding region. G47Δ was derived from G207 by deleting 312 bp from the ICP47 locus, as indicated. (b) Map of the ICP47 locus showing locations of the overlapping 3′ coterminal transcripts (US10, US11, and ICP47), ORFs (thick arrow), and ICP47 splice junctions (∧). (c) Map of plasmid pIE12Δ used to generate deletion by homologous recombination with the indicated flanking sequences. Whereas US11 is regulated as a true late gene in wild-type HSV-1, deletion between the indicated BstEII and EcoNI sites places US11 under control of the ICP47 immediate-early promoter. Restriction site abbreviations: B, BamHI; Bs, BstEII; EN, EcoNI; Nr, NruI; E, EcoRI.