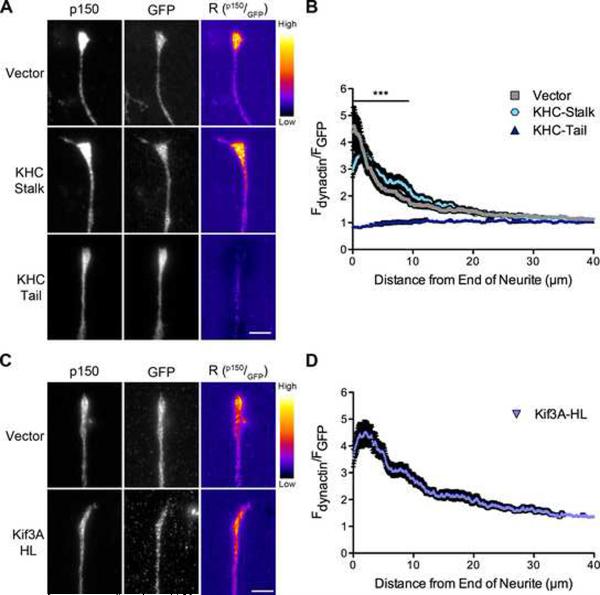
Figure 3. Kinesin-1, but not kinesin-2, contributes to the distal localization of dynactin.
(A) Distal ends of DRG neurons expressing GFP, GFP-tagged KHC-stalk or GFP-tagged KHC-tail were stained at 2 DIV for endogenous p150Glued and GFP. These images were individually contrast enhanced to display both axonal and tip staining. The raw p150 data was divided by the corresponding raw GFP signal to create the ratio-image (Rp150/GFP). These images show the distal accumulation relative to GFP. These ratio-images were contrast enhanced to the same level and a heat map was applied to show the relative intensities of the ratio. The warmer colors represent a higher ratio, while cooler colors represent a lower ratio. (B) Line-scan quantification of the distal accumulation. The normalized ratio of endogenous dynactin fluorescence intensity to GFP intensity was determined along the length of the neurite tip. The KHC-tail, a dominant-negative kinesin-1 inhibitor, significantly disrupted the localization of dynactin over the distal 9 μm of the neurite as compared to vector expressing neurons. Mean ± SEM, n≥46 neurite tips from 7–8 neurons per condition, ***P<0.001, two-way ANOVA Bonferroni post test. (C) Distal ends of DRG neurons expressing GFP or GFP-tagged Kif3A-HL, a dominant-negative kinesin-2 inhibitor, were stained at 2 DIV for endogenous p150Glued and GFP. These images were individually contrast enhanced to display both axonal and tip staining. The ratio-images (Rp150/GFP) were calculated from the raw imaging data and a heat map was applied as described in (A). (D) Line-scan quantification of the distal accumulation as described in (B). Kif3A-HL expression had no effect on the distal accumulation of dynactin. Mean ± SEM, n≥46 neurite tips from 7 neurons per condition. Also see Figure S3.