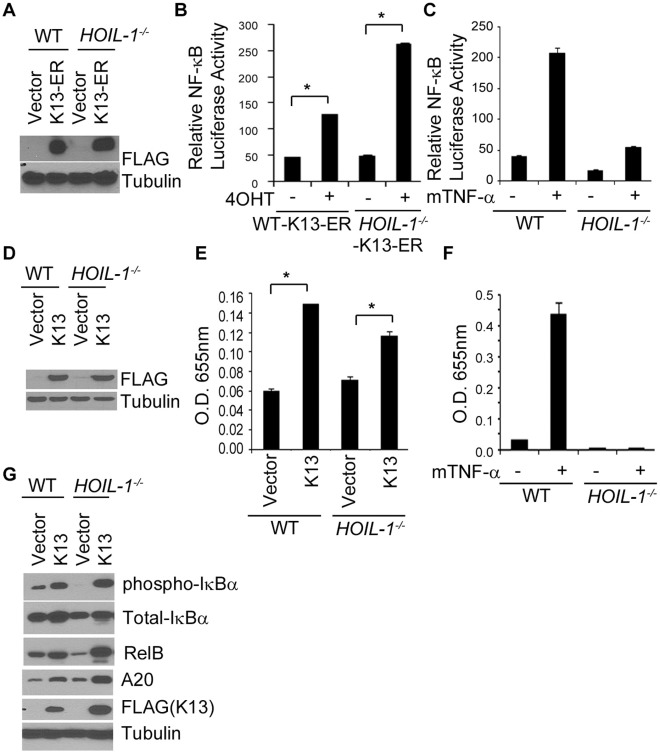
Figure 3. HOIL-1 is not essential for K13-induced NF-κB activation.
A. The expression of FLAG-tagged K13-ERTAM in wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEF was confirmed with Western blotting. The blot was re-probed with a tubulin antibody to show equal protein loading. B. Wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs stably expressing FLAG-K13-ERTAM were transfected with NF-κB-Luc and Renilla reporter constructs. Cells were subsequently treated with 4OHT (20 nM) for 48 hours and the luciferase reporter assay was performed essentially as described in Figure 1A. Asterisks (*) indicate significance at levels of p≤0.05 as compared to vehicle-treated cells. C. Wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs were transfected with NF-κB-Luc and Renilla reporter constructs and 6 hours post-transfection, these cells were treated with mTNF-α (10ng/ml) for 18 hours and the luciferase reporter assay was performed essentially as described in Figure 1A. D. Expression of transduced FLAG-tagged K13 in wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs was examined by immunoblot analysis; tubulin was used as a loading control. E. Nuclear p65 DNA binding activities in the nuclear extracts of wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs expressing an empty vector or FLAG-K13. Asterisks (*) indicate significance at levels of p≤0.05 as compared to vector cells. F. Nuclear p65 DNA binding activities in the nuclear extracts of wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs following treatment with murine TNFα. G. Wild-type and HOIL-1−/− MEFs expressing FLAG-K13 were examined for NF-κB activation by Western blot analysis using antibodies against phospho-IκBα, Total IκBα, A20 and RelB. The blot was re-probed with FLAG and Tubulin antibodies to check the expression of the transduced K13 and equal protein loading, respectively.