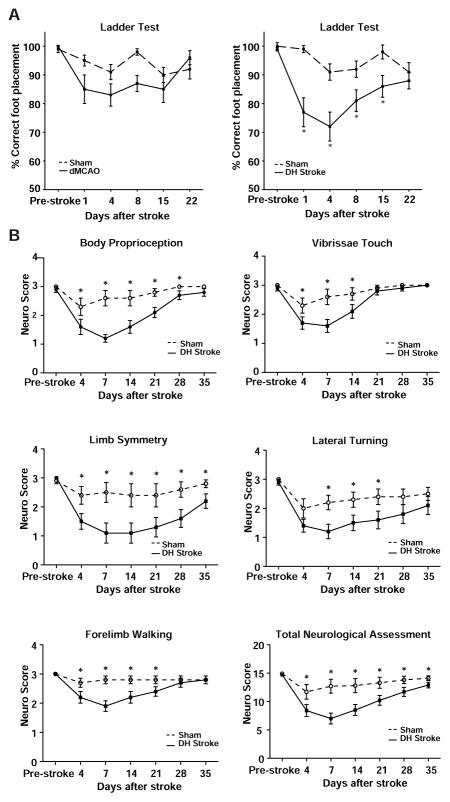
Figure 5.
The DH model of stroke causes a behavioral deficit. A) Mice that underwent right side DH stroke showed significant hemiparesis in the left front paw for 15 days following stroke. Mice that underwent sham DH stroke (hypoxia + craniectomy, but no ligation of the MCA), sham dMCAO (craniectomy but no ligation of the MCA) or dMCAO did not have significant ladder deficits. Groups have been separated onto two graphs for clarity. * p<0.05 compared to sham by one way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. B) Neurological evaluation reveals a sensory and motor deficit after DH stroke. Mice that underwent right side DH stroke showed significant sensory deficits in body proprioception and vibrissae touch. They also had significant motor deficits in limb symmetry, lateral turning ability and forelimb walking ability. * P<0.05 by Student’s t-test compared to mice that underwent sham DH stroke. Error bars are SEM.