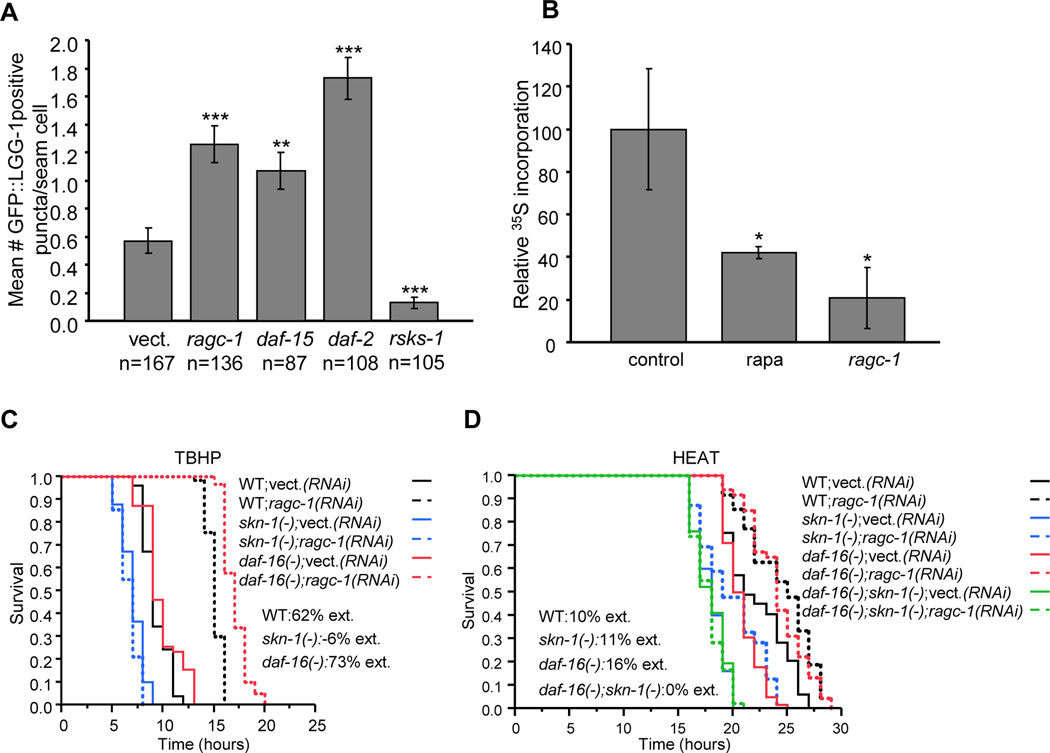
Figure 1. Genetic TORC1 inhibition increases stress resistance through SKN-1 and DAF-16.
(A) Increased autophagy after TORC1-pathway gene knockdown. LGG- 1::GFP puncta were counted in seam cells (n) in day 3 adults. ***P≤0.0001, **P<0.001, unpaired t-test. (B) Decreased protein synthesis after genetic TORC1 inhibition or rapamycin treatment. *P≤0.005, Student’s one-sided t-test. Error bars represent ± SEM (C) TORC1 inhibition by ragc-1 RNAi increased oxidative stress (TBHP) resistance dependent upon skn-1 but not daf-16. The skn-1(zu67) and daf-16(mgDf47) alleles were analyzed in all experiments unless otherwise indicated. In all survival plots, ext. refers to mean survival extension associated with the indicated intervention, and WT to the wild type. The y-axis indicates proportion surviving. (D) Increased resistance to heat (35°C) is mediated by both skn-1 and daf-16. Representative experiments are shown in (A-D). Statistics and stress resistance analyses of additional TORC1 pathway genes are provided in Tables S1 and S2.