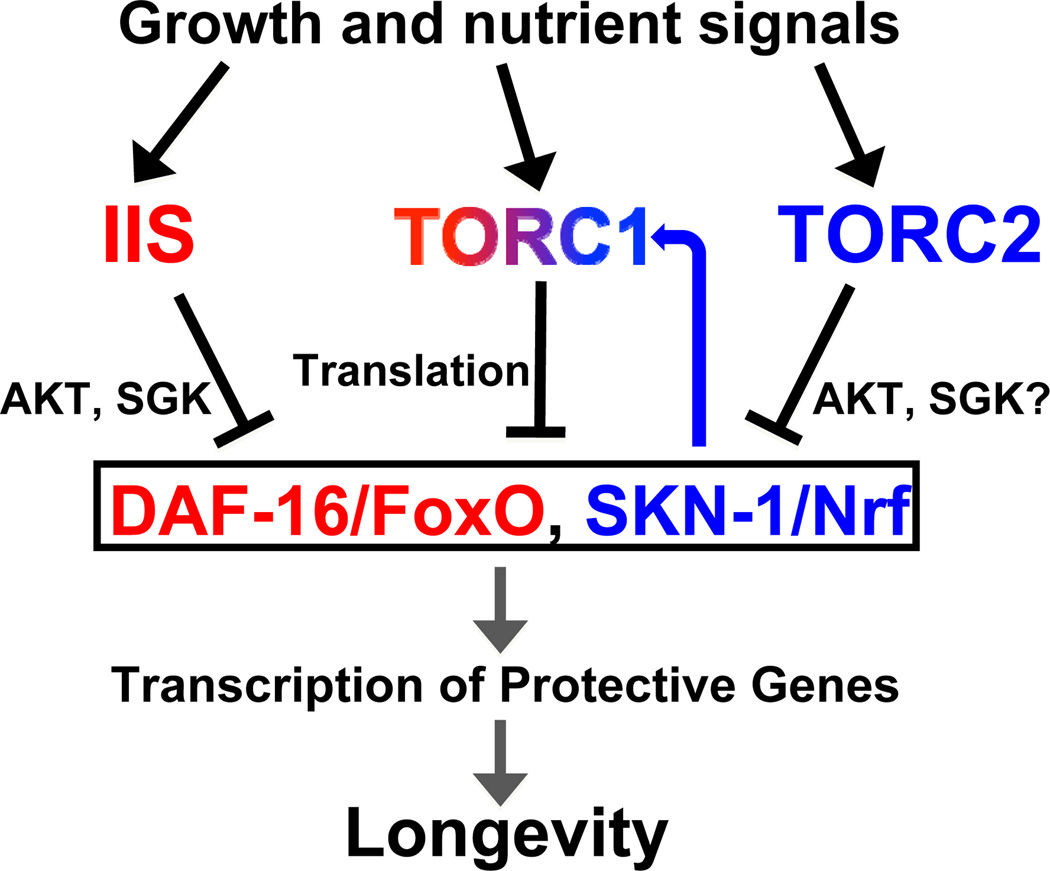
Figure 7. Regulation of SKN-1 and DAF-16 by TOR signaling.
The IIS, TORC1, and TORC2 pathways are involved in growth (see text). IIS inhibits SKN-1 and DAF-16 directly, through phosphorylation. TORC1 inhibits SKN-1 and DAF-16 expression and activity, at least in part by increasing mRNA translation. TORC2 regulates SKN-1 nuclear occupancy in a nutrient-dependent manner. DAF-16 is required for longevity that derives from inhibiting IIS or TORC1, but not TORC2. SKN-1 plays a contributory role in the effects of IIS on longevity, but is essential for TORC1 or TORC2 inhibition to extend lifespan. When TORC1 is inhibited, SKN-1 increases transcription of TORC1 pathway genes in a feedback loop.